Page 182 - Anatomy and Physiology of Farm Animals, 8th Edition
P. 182
The Equine Foot and Passive Stay Apparatus / 167
(A) (B)
VetBooks.ir
M. quadriceps
femoris
M. triceps
M. biceps brachii
brachii
Superficial digital
flexor m.
Lacertus fibrosis
Fascia of M. extensor
carpi radialis
M. fibularis tertius
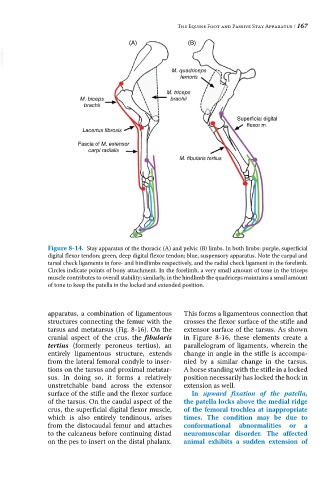
Figure 8-14. Stay apparatus of the thoracic (A) and pelvic (B) limbs. In both limbs: purple, superficial
digital flexor tendon; green, deep digital flexor tendon; blue, suspensory apparatus. Note the carpal and
tarsal check ligaments in fore‐ and hindlimbs respectively, and the radial check ligament in the forelimb.
Circles indicate points of bony attachment. In the forelimb, a very small amount of tone in the triceps
muscle contributes to overall stability; similarly, in the hindlimb the quadriceps maintains a small amount
of tone to keep the patella in the locked and extended position.
apparatus, a combination of ligamentous This forms a ligamentous connection that
structures connecting the femur with the crosses the flexor surface of the stifle and
tarsus and metatarsus (Fig. 8‐16). On the extensor surface of the tarsus. As shown
cranial aspect of the crus, the fibularis in Figure 8‐16, these elements create a
tertius (formerly peroneus tertius), an parallelogram of ligaments, wherein the
entirely ligamentous structure, extends change in angle in the stifle is accompa-
from the lateral femoral condyle to inser- nied by a similar change in the tarsus.
tions on the tarsus and proximal metatar- A horse standing with the stifle in a locked
sus. In doing so, it forms a relatively position necessarily has locked the hock in
unstretchable band across the extensor extension as well.
surface of the stifle and the flexor surface In upward fixation of the patella,
of the tarsus. On the caudal aspect of the the patella locks above the medial ridge
crus, the superficial digital flexor muscle, of the femoral trochlea at inappropriate
which is also entirely tendinous, arises times. The condition may be due to
from the distocaudal femur and attaches conformational abnormalities or a
to the calcaneus before continuing distad neuromuscular disorder. The affected
on the pes to insert on the distal phalanx. animal exhibits a sudden extension of