Page 207 - Anatomy and Physiology of Farm Animals, 8th Edition
P. 207
192 / Anatomy and Physiology of Farm Animals
The CNS receives information arriving conduct electrical signals away from the
cell bodies. The axon (each neuron gives
via the PNS, integrates that information,
VetBooks.ir and initiates appropriate movement of rise to only one, which usually branches)
arises from a conical projection of the cell,
body parts, glandular secretion, or behav-
ior in response. It may do this via voluntary the axon hillock, and its terminus branches
or involuntary (i.e., autonomic or reflexive) into an arborization called the teloden-
processing. Communication between the drion. The telodendrion makes contact
CNS and the target muscles and glands in with other neurons or effector organs (tar-
the periphery is accomplished via motor gets), such as muscle or glandular tissue.
(efferent) nerves of the PNS. In general terms, aggregates of neuronal
cell bodies form the gray matter of the CNS,
whereas regions characterized primarily
Microscopic Neuroanatomy by bundles of axons are white matter
(Table 10‐1). Gray matter of the CNS is gen-
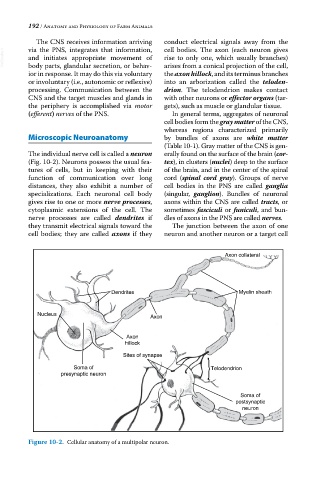
The individual nerve cell is called a neuron erally found on the surface of the brain (cor-
(Fig. 10‐2). Neurons possess the usual fea- tex), in clusters (nuclei) deep to the surface
tures of cells, but in keeping with their of the brain, and in the center of the spinal
function of communication over long cord (spinal cord gray). Groups of nerve
distances, they also exhibit a number of cell bodies in the PNS are called ganglia
specializations. Each neuronal cell body (singular, ganglion). Bundles of neuronal
gives rise to one or more nerve processes, axons within the CNS are called tracts, or
cytoplasmic extensions of the cell. The sometimes fasciculi or funiculi, and bun-
nerve processes are called dendrites if dles of axons in the PNS are called nerves.
they transmit electrical signals toward the The junction between the axon of one
cell bodies; they are called axons if they neuron and another neuron or a target cell
Axon collateral
Dendrites Myelin sheath
Nucleus Axon
Axon
hillock
Sites of synapse
Soma of Telodendrion
presynaptic neuron
Soma of
postsynaptic
neuron
Figure 10-2. Cellular anatomy of a multipolar neuron.