Page 210 - Anatomy and Physiology of Farm Animals, 8th Edition
P. 210
Anatomy of the Nervous System / 195
closes later. Failure of closure in the cau-
VetBooks.ir dal part of the neural tube results in a
variety of spinal cord abnormalities
called myelodysplasias. These are some-
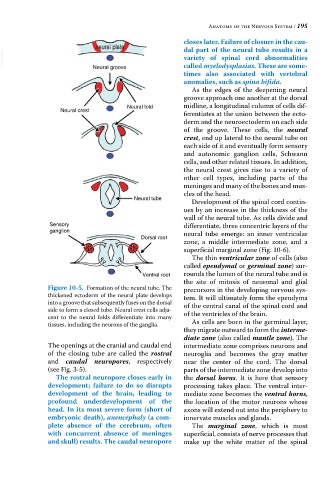
Neural groove
times also associated with vertebral
anomalies, such as spina bifida.
As the edges of the deepening neural
groove approach one another at the dorsal
Neural fold midline, a longitudinal column of cells dif-
Neural crest
ferentiates at the union between the ecto-
derm and the neuroectoderm on each side
of the groove. These cells, the neural
crest, end up lateral to the neural tube on
each side of it and eventually form sensory
and autonomic ganglion cells, Schwann
cells, and other related tissues. In addition,
the neural crest gives rise to a variety of
other cell types, including parts of the
meninges and many of the bones and mus-
cles of the head.
Neural tube
Development of the spinal cord contin-
ues by an increase in the thickness of the
wall of the neural tube. As cells divide and
Sensory differentiate, three concentric layers of the
ganglion neural tube emerge: an inner ventricular
Dorsal root
zone, a middle intermediate zone, and a
superficial marginal zone (Fig. 10‐6).
The thin ventricular zone of cells (also
called ependymal or germinal zone) sur-
Ventral root rounds the lumen of the neural tube and is
the site of mitosis of neuronal and glial
Figure 10-5. Formation of the neural tube. The precursors in the developing nervous sys-
thickened ectoderm of the neural plate develops tem. It will ultimately form the ependyma
into a groove that subsequently fuses on the dorsal of the central canal of the spinal cord and
side to form a closed tube. Neural crest cells adja-
cent to the neural folds differentiate into many of the ventricles of the brain.
tissues, including the neurons of the ganglia. As cells are born in the germinal layer,
they migrate outward to form the interme-
diate zone (also called mantle zone). The
The openings at the cranial and caudal end intermediate zone comprises neurons and
of the closing tube are called the rostral neuroglia and becomes the gray matter
and caudal neuropores, respectively near the center of the cord. The dorsal
(see Fig. 3‐5). parts of the intermediate zone develop into
The rostral neuropore closes early in the dorsal horns. It is here that sensory
development; failure to do so disrupts processing takes place. The ventral inter-
development of the brain, leading to mediate zone becomes the ventral horns,
profound underdevelopment of the the location of the motor neurons whose
head. In its most severe form (short of axons will extend out into the periphery to
embryonic death), anencephaly (a com- innervate muscles and glands.
plete absence of the cerebrum, often The marginal zone, which is most
with concurrent absence of meninges superficial, consists of nerve processes that
and skull) results. The caudal neuropore make up the white matter of the spinal