Page 37 - Veterinary Laser Therapy in Small Animal Practice
P. 37
Analgesic effect 23
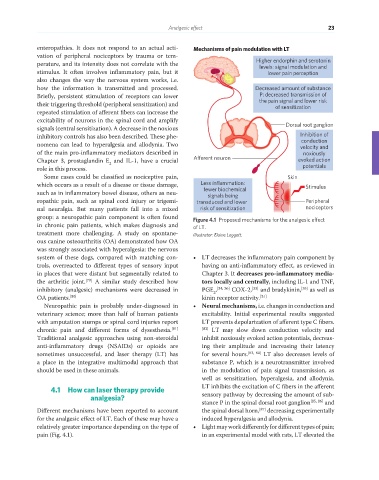
enteropathies. It does not respond to an actual acti- Mechanisms of pain modulation with LT
vation of peripheral nociceptors by trauma or tem-
perature, and its intensity does not correlate with the Higher endorphin and serotonin
levels: signal modulation and
stimulus. It often involves inflammatory pain, but it lower pain perception
also changes the way the nervous system works, i.e.
how the information is transmitted and processed. Decreased amount of substance
Briefly, persistent stimulation of receptors can lower P: decreased transmission of
their triggering threshold (peripheral sensitization) and the pain signal and lower risk
of sensitization
repeated stimulation of afferent fibers can increase the
excitability of neurons in the spinal cord and amplify Dorsal root ganglion
signals (central sensitization). A decrease in the noxious
inhibitory controls has also been described. These phe- Inhibition of
conduction
nomena can lead to hyperalgesia and allodynia. Two velocity and
of the main pro-inflammatory mediators described in noxiously
Chapter 3, prostaglandin E and IL-1, have a crucial A erent neuron evoked action
2
role in this process. potentials
Some cases could be classified as nociceptive pain, Skin
which occurs as a result of a disease or tissue damage, Less inflammation: Stimulus
such as in inflammatory bowel disease, others as neu- fewer biochemical
signals being
ropathic pain, such as spinal cord injury or trigemi- transduced and lower Peripheral
nal neuralgia. But many patients fall into a mixed risk of sensitization nociceptors
group: a neuropathic pain component is often found Figure 4.1 Proposed mechanisms for the analgesic effect
in chronic pain patients, which makes diagnosis and of LT.
treatment more challenging. A study on spontane- Illustrator: Elaine Leggett.
ous canine osteoarthritis (OA) demonstrated how OA
was strongly associated with hyperalgesia: the nervous
system of these dogs, compared with matching con- • LT decreases the inflammatory pain component by
trols, overreacted to different types of sensory input having an anti-inflammatory effect, as reviewed in
in places that were distant but segmentally related to Chapter 3. It decreases pro-inflammatory media-
the arthritic joint. [79] A similar study described how tors locally and centrally, including IL-1 and TNF,
inhibitory (analgesic) mechanisms were decreased in PGE , [34, 36] COX-2, [33] and bradykinin, [35] as well as
2
OA patients. [80] kinin receptor activity. [31]
Neuropathic pain is probably under-diagnosed in • Neural mechanisms, i.e. changes in conduction and
veterinary science; more than half of human patients excitability. Initial experimental results suggested
with amputation stumps or spinal cord injuries report LT prevents depolarization of afferent type C fibers.
chronic pain and different forms of dysesthesia. [81] [82] LT may slow down conduction velocity and
Traditional analgesic approaches using non-steroidal inhibit noxiously evoked action potentials, decreas-
anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) or opioids are ing their amplitude and increasing their latency
sometimes unsuccessful, and laser therapy (LT) has for several hours. [83, 84] LT also decreases levels of
a place in the integrative multimodal approach that substance P, which is a neurotransmitter involved
should be used in these animals. in the modulation of pain signal transmission, as
well as sensitization, hyperalgesia, and allodynia.
4.1 How can laser therapy provide LT inhibits the excitation of C fibers in the afferent
analgesia? sensory pathway by decreasing the amount of sub-
stance P in the spinal dorsal root ganglion [85, 86] and
Different mechanisms have been reported to account the spinal dorsal horn, [87] decreasing experimentally
for the analgesic effect of LT. Each of these may have a induced hyperalgesia and allodynia.
relatively greater importance depending on the type of • Light may work differently for different types of pain;
pain (Fig. 4.1). in an experimental model with rats, LT elevated the
REDONDO PRINT (4-COL BLEED).indd 23 08/08/2019 09:47