Page 126 - Veterinary Histology of Domestic Mammals and Birds, 5th Edition
P. 126
108 Veterinary Histology of Domestic Mammals and Birds
VetBooks.ir
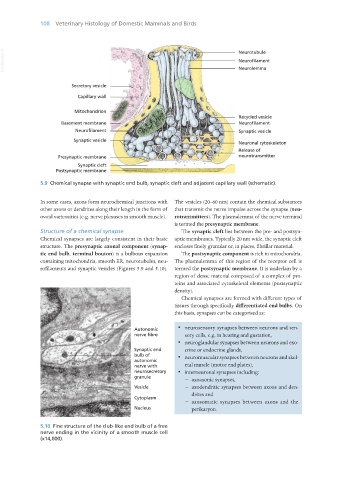
5.9 Chemical synapse with synaptic end bulb, synaptic cleft and adjacent capillary wall (schematic).
In some cases, axons form neurochemical junctions with The vesicles (20–60 nm) contain the chemical substances
other axons or dendrites along their length in the form of that transmit the nerve impulse across the synapse (neu-
ovoid varicosities (e.g. nerve plexuses in smooth muscle). rotransmitters). The plasmalemma of the nerve terminal
is termed the presynaptic membrane.
Structure of a chemical synapse The synaptic cleft lies between the pre- and postsyn-
Chemical synapses are largely consistent in their basic aptic membranes. Typically 20 nm wide, the synaptic cleft
structure. The presynaptic axonal component (synap- encloses finely granular or, in places, fibrillar material.
tic end bulb, terminal bouton) is a bulbous expansion The postsynaptic component is rich in mitochondria.
containing mitochondria, smooth ER, neurotubules, neu- The plasmalemma of this region of the receptor cell is
rofilaments and synaptic vesicles (Figures 5.9 and 5.10). termed the postsynaptic membrane. It is underlain by a
region of dense material composed of a complex of pro-
teins and associated cytoskeletal elements (postsynaptic
density).
Chemical synapses are formed with different types of
tissues through specifically differentiated end bulbs. On
this basis, synapses can be categorised as:
· neurosensory synapses between neurons and sen-
sory cells, e.g. in hearing and gustation,
· neuroglandular synapses between neurons and exo-
crine or endocrine glands,
· neuromuscular synapses between neurons and skel-
etal muscle (motor end plates),
· interneuronal synapses including:
− axoaxonic synapses,
− axodendritic synapses between axons and den-
drites and
− axosomatic synapses between axons and the
perikaryon.
5.10 Fine structure of the club-like end bulb of a free
nerve ending in the vicinity of a smooth muscle cell
(x14,000).
Vet Histology.indb 108 16/07/2019 14:57