Page 156 - Veterinary Histology of Domestic Mammals and Birds, 5th Edition
P. 156
138 Veterinary Histology of Domestic Mammals and Birds
Proliferation Maturation
VetBooks.ir
Neutrophil
Basophil
Eosinophil
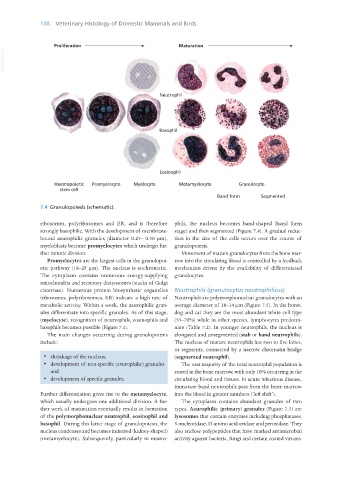
Haemopoietic Promyelocyte Myelocyte Metamyelocyte Granulocyte
stem cell
Band form Segmented
7.4 Granulopoiesis (schematic).
ribosomes, polyribosomes and ER, and is therefore phils, the nucleus becomes band-shaped (band form
strongly basophilic. With the development of membrane- stage) and then segmented (Figure 7.4). A gradual reduc-
bound azurophilic granules (diameter 0.25– 0.50 μm), tion in the size of the cells occurs over the course of
myeloblasts become promyelocytes which undergo fur- granulopoiesis.
ther mitotic division. Movement of mature granulocytes from the bone mar-
Promyelocytes are the largest cells in the granulopoi- row into the circulating blood is controlled by a feedback
etic pathway (18–25 μm). The nucleus is euchromatic. mechanism driven by the availability of differentiated
The cytoplasm contains numerous energy-supplying granulocytes.
mitochondria and secretory dictyosomes (stacks of Golgi
cisternae). Numerous protein biosynthetic organelles Neutrophils (granulocytus neutrophilicus)
(ribosomes, polyribosomes, ER) indicate a high rate of Neutrophils are polymorphonuclear granulocytes with an
metabolic activity. Within a week, the azurophilic gran- average diameter of 10–14 μm (Figure 7.5). In the horse,
ules differentiate into specific granules. As of this stage, dog and cat they are the most abundant white cell type
(myelocyte), recognition of neutrophils, eosinophils and (55–70%) while in other species, lymphocytes predomi-
basophils becomes possible (Figure 7.4). nate (Table 7.2). In younger neutrophils, the nucleus is
The main changes occurring during granulopoiesis elongated and unsegmented (stab or band neutrophils).
include: The nucleus of mature neutrophils has two to five lobes,
or segments, connected by a narrow chromatin bridge
· shrinkage of the nucleus, (segmented neutrophil).
· development of non-specific (azurophilic) granules The vast majority of the total neutrophil population is
and stored in the bone marrow, with only 10% occurring in the
· development of specific granules. circulating blood and tissues. In acute infectious disease,
immature band neutrophils pass from the bone marrow
Further differentiation gives rise to the metamyelocyte, into the blood in greater numbers (‘left shift’).
which usually undergoes one additional division. A fur- The cytoplasm contains abundant granules of two
ther week of maturation eventually results in formation types. Azurophilic (primary) granules (Figure 7.5) are
of the polymorphonuclear neutrophil, eosinophil and lysosomes that contain enzymes including phosphatases,
basophil. During this latter stage of granulopoiesis, the 5-nucleotidase, D-amino acid oxidase and peroxidase. They
nucleus condenses and becomes indented (kidney-shaped) also enclose polypeptides that have marked antimicrobial
(metamyelocyte). Subsequently, particularly in neutro- activity against bacteria, fungi and certain coated viruses.
Vet Histology.indb 138 16/07/2019 14:58