Page 24 - Veterinary Histology of Domestic Mammals and Birds, 5th Edition
P. 24
6 Veterinary Histology of Domestic Mammals and Birds
VetBooks.ir
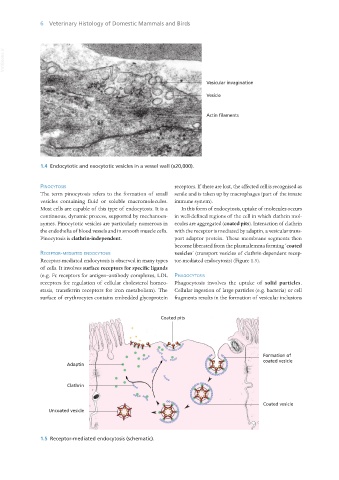
1.4 Endocytotic and exocytotic vesicles in a vessel wall (x20,000).
Pinocytosis receptors. If these are lost, the affected cell is recognised as
The term pinocytosis refers to the formation of small senile and is taken up by macrophages (part of the innate
vesicles containing fluid or soluble macromolecules. immune system).
Most cells are capable of this type of endocytosis. It is a In this form of endocytosis, uptake of molecules occurs
continuous, dynamic process, supported by mechanoen- in well-defined regions of the cell in which clathrin mol-
zymes. Pinocytotic vesicles are particularly numerous in ecules are aggregated (coated pits). Interaction of clathrin
the endothelia of blood vessels and in smooth muscle cells. with the receptor is mediated by adaptin, a vesicular trans-
Pinocytosis is clathrin-independent. port adaptor protein. These membrane segments then
become liberated from the plasmalemma forming ‘coated
RecePtoR-mediated endocytosis vesicles’ (transport vesicles of clathrin-dependent recep-
Receptor-mediated endocytosis is observed in many types tor-mediated endocytosis) (Figure 1.5).
of cells. It involves surface receptors for specific ligands
(e.g. Fc receptors for antigen–antibody complexes, LDL Phagocytosis
receptors for regulation of cellular cholesterol homeo- Phagocytosis involves the uptake of solid particles.
stasis, transferrin receptors for iron metabolism). The Cellular ingestion of large particles (e.g. bacteria) or cell
surface of erythrocytes contains embedded glycoprotein fragments results in the formation of vesicular inclusions
1.5 Receptor-mediated endocytosis (schematic).
Vet Histology.indb 6 16/07/2019 14:52