Page 369 - Veterinary Histology of Domestic Mammals and Birds, 5th Edition
P. 369
Receptors and sense organs (organa sensuum) 351
In some regions, the lamina propria mucosae contains scribed areas of the nasal mucosa and in the vomeronasal
VetBooks.ir serous, tubulo-acinar glands (gustatory glands). The organ.
The olfactory epithelium is pseudostratified and con-
secretory product empties via excretory ducts into the
sulcus of vallate papillae and sometimes into the spaces tains three cell types:
between foliate papillae. The watery secretion rinses the
taste buds, permitting the detection of new stimuli. The · neurosensory cells,
number of glands increases with the number of taste buds. · supporting cells and
· basal cells.
Olfactory organs (organa olfactus)
In animals, the olfactory sense plays an important role The perikarya of the neurosensory cells (bipolar neu-
in acquisition of food, identification of conspecifics and rons) are located in the epithelium, the cell nuclei lying
sexual behaviour. Domestic mammals are considered approximately at mid-epithelial level. The cells are pear- to
macro-osmatic animals (those with highly developed bottle-shaped and are flanked by supporting cells. At the
organs of smell). Olfactory stimuli are detected in the epithelial surface, the dendritic process of the neurosen-
olfactory mucosa (tunica mucosa olfactoria). The mucosa sory cell ends in a club-shaped expansion (dendritic bulb)
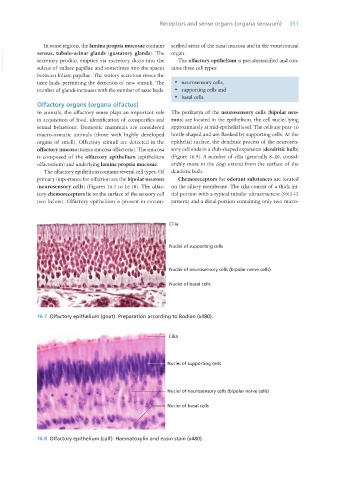
is composed of the olfactory epithelium (epithelium (Figure 16.9). A number of cilia (generally 8–20, consid-
olfactorium) and underlying lamina propria mucosae. erably more in the dog) extend from the surface of the
The olfactory epithelium contains several cell types. Of dendritic bulb.
primary importance for olfaction are the bipolar neurons Chemoreceptors for odorant substances are located
(neurosensory cells) (Figures 16.7 to 16.10). The olfac- on the ciliary membrane. The cilia consist of a thick ini-
tory chemoreceptors lie on the surface of the sensory cell tial portion with a typical tubular ultrastructure (9×2+2
(see below). Olfactory epithelium is present in circum- pattern) and a distal portion containing only two micro-
16.7 Olfactory epithelium (goat). Preparation according to Bodian (x480).
16.8 Olfactory epithelium (calf). Haematoxylin and eosin stain (x480).
Vet Histology.indb 351 16/07/2019 15:07