Page 46 - Veterinary Histology of Domestic Mammals and Birds, 5th Edition
P. 46
28 Veterinary Histology of Domestic Mammals and Birds
VetBooks.ir
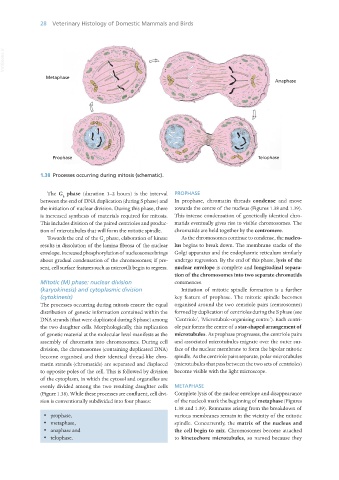
1.38 Processes occurring during mitosis (schematic).
The G phase (duration 1–2 hours) is the interval PROPHASE
2
between the end of DNA duplication (during S phase) and In prophase, chromatin threads condense and move
the initiation of nuclear division. During this phase, there towards the centre of the nucleus (Figures 1.38 and 1.39).
is increased synthesis of materials required for mitosis. This intense condensation of genetically identical chro-
This includes division of the paired centrioles and produc- matids eventually gives rise to visible chromosomes. The
tion of microtubules that will form the mitotic spindle. chromatids are held together by the centromere.
Towards the end of the G phase, elaboration of kinase As the chromosomes continue to condense, the nucleo-
2
results in dissolution of the lamina fibrosa of the nuclear lus begins to break down. The membrane stacks of the
envelope. Increased phosphorylation of nucleosomes brings Golgi apparatus and the endoplasmic reticulum similarly
about gradual condensation of the chromosomes; if pre- undergo regression. By the end of this phase, lysis of the
sent, cell surface features such as microvilli begin to regress. nuclear envelope is complete and longitudinal separa-
tion of the chromosomes into two separate chromatids
Mitotic (M) phase: nuclear division commences.
(karyokinesis) and cytoplasmic division Initiation of mitotic spindle formation is a further
(cytokinesis) key feature of prophase. The mitotic spindle becomes
The processes occurring during mitosis ensure the equal organised around the two centriole pairs (centrosomes)
distribution of genetic information contained within the formed by duplication of centrioles during the S phase (see
DNA strands (that were duplicated during S phase) among ‘Centriole’, ‘Microtubule-organising centre’). Each centri-
the two daughter cells. Morphologically, this replication ole pair forms the centre of a star-shaped arrangement of
of genetic material at the molecular level manifests as the microtubules. As prophase progresses, the centriole pairs
assembly of chromatin into chromosomes. During cell and associated microtubules migrate over the outer sur-
division, the chromosomes (containing duplicated DNA) face of the nuclear membrane to form the bipolar mitotic
become organised and their identical thread-like chro- spindle. As the centriole pairs separate, polar microtubules
matin strands (chromatids) are separated and displaced (microtubules that pass between the two sets of centrioles)
to opposite poles of the cell. This is followed by division become visible with the light microscope.
of the cytoplasm, in which the cytosol and organelles are
evenly divided among the two resulting daughter cells METAPHASE
(Figure 1.38). While these processes are confluent, cell divi- Complete lysis of the nuclear envelope and disappearance
sion is conventionally subdivided into four phases: of the nucleoli mark the beginning of metaphase (Figures
1.38 and 1.39). Remnants arising from the breakdown of
· prophase, various membranes remain in the vicinity of the mitotic
· metaphase, spindle. Concurrently, the matrix of the nucleus and
· anaphase and the cell begin to mix. Chromosomes become attached
· telophase. to kinetochore microtubules, so named because they
Vet Histology.indb 28 16/07/2019 14:53