Page 98 - Veterinary Histology of Domestic Mammals and Birds, 5th Edition
P. 98
80 Veterinary Histology of Domestic Mammals and Birds
VetBooks.ir
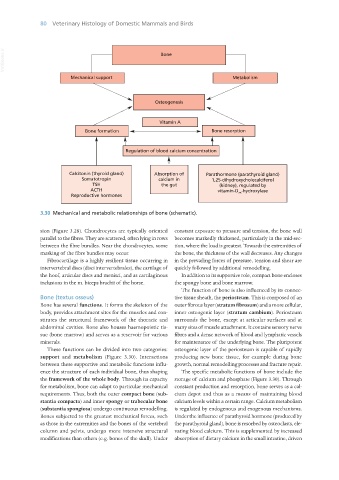
3.30 Mechanical and metabolic relationships of bone (schematic).
sion (Figure 3.28). Chondrocytes are typically oriented constant exposure to pressure and tension, the bone wall
parallel to the fibres. They are scattered, often lying in rows becomes markedly thickened, particularly in the mid-sec-
between the fibre bundles. Near the chondrocytes, some tion, where the load is greatest. Towards the extremities of
masking of the fibre bundles may occur. the bone, the thickness of the wall decreases. Any changes
Fibrocartilage is a highly resilient tissue occurring in in the prevailing forces of pressure, tension and shear are
intervertebral discs (disci intervertebrales), the cartilage of quickly followed by additional remodelling.
the hoof, articular discs and menisci, and as cartilaginous In addition to its supportive role, compact bone encloses
inclusions in the m. biceps brachii of the horse. the spongy bone and bone marrow.
The function of bone is also influenced by its connec-
Bone (textus osseus) tive tissue sheath, the periosteum. This is composed of an
Bone has several functions. It forms the skeleton of the outer fibrous layer (stratum fibrosum) and a more cellular,
body, provides attachment sites for the muscles and con- inner osteogenic layer (stratum cambium). Periosteum
stitutes the structural framework of the thoracic and surrounds the bone, except at articular surfaces and at
abdominal cavities. Bone also houses haemopoietic tis- many sites of muscle attachment. It contains sensory nerve
sue (bone marrow) and serves as a reservoir for various fibres and a dense network of blood and lymphatic vessels
minerals. for maintenance of the underlying bone. The pluripotent
These functions can be divided into two categories: osteogenic layer of the periosteum is capable of rapidly
support and metabolism (Figure 3.30). Interactions producing new bone tissue, for example during bone
between these supportive and metabolic functions influ- growth, normal remodelling processes and fracture repair.
ence the structure of each individual bone, thus shaping The specific metabolic functions of bone include the
the framework of the whole body. Through its capacity storage of calcium and phosphate (Figure 3.30). Through
for metabolism, bone can adapt to particular mechanical constant production and resorption, bone serves as a cal-
requirements. Thus, both the outer compact bone (sub- cium depot and thus as a means of maintaining blood
stantia compacta) and inner spongy or trabecular bone calcium levels within a certain range. Calcium metabolism
(substantia spongiosa) undergo continuous remodelling. is regulated by endogenous and exogenous mechanisms.
Bones subjected to the greatest mechanical forces, such Under the influence of parathyroid hormone (produced by
as those in the extremities and the bones of the vertebral the parathyroid gland), bone is resorbed by osteoclasts, ele-
column and pelvis, undergo more intensive structural vating blood calcium. This is supplemented by increased
modifications than others (e.g. bones of the skull). Under absorption of dietary calcium in the small intestine, driven
Vet Histology.indb 80 16/07/2019 14:56