Page 103 - Veterinary Histology of Domestic Mammals and Birds, 5th Edition
P. 103
Connective and supportive tissues (textus connectivus) 85
Individual crystals are needle-shaped (20–40 nm long, 2–3 jected over extended periods to forces of pressure and
VetBooks.ir nm wide). The stability of bone results from the connection tension. This type of bone is thus found wherever new
bone is formed.
between the hydroxyapatite crystals and the collagen fibres.
Woven bone is laid down during embryonic develop-
Types of bone ment. After birth, it is rapidly replaced with more highly
Histologically, bone tissue can be divided into two types: differentiated lamellar bone. In certain locations, such as
the osseous labyrinth of the inner ear, the external acoustic
· woven bone (os membranaceum reticulofibrosum) meatus and at the attachment sites of large tendons, woven
and bone is retained throughout the life of the animal.
· lamellar bone (os membranaceum lamellosum). Woven bone has a relatively high cell population,
including osteocytes that are distributed randomly
The same cell types are found in both types of bone, and throughout the mineralised matrix. The ground substance
both contain collagen and minerals. The principal differ- is interspersed with an irregular network of collagen fibres
ences between them are the organisation of the collagen comprising bundles of large and small fibrils that are not
fibres within the matrix and the proportion of cells and aligned in any particular direction. The mineral content of
ground substance. woven bone is lower than that of lamellar bone.
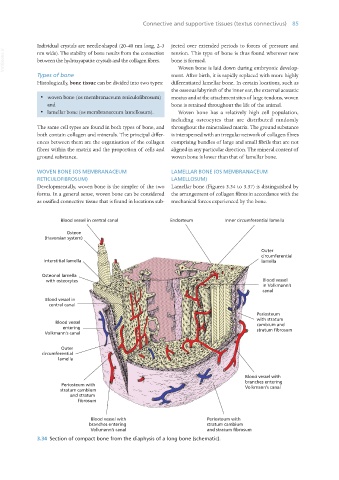
WOVEN BONE (OS MEMBRANACEUM LAMELLAR BONE (OS MEMBRANACEUM
RETICULOFIBROSUM) LAMELLOSUM)
Developmentally, woven bone is the simpler of the two Lamellar bone (Figures 3.34 to 3.37) is distinguished by
forms. In a general sense, woven bone can be considered the arrangement of collagen fibres in accordance with the
as ossified connective tissue that is found in locations sub- mechanical forces experienced by the bone.
Blood vessel in central canal Endosteum Inner circumferential lamella
Osteon
(Haversian system)
Outer
circumferential
Interstitial lamella lamella
Osteonal lamella
with osteocytes Blood vessel
in Volkmann’s
canal
Blood vessel in
central canal
Periosteum
with stratum
Blood vessel cambium and
entering stratum fibrosum
Volkmann’s canal
Outer
circumferential
lamella
Blood vessel with
branches entering
Periosteum with Volkmann’s canal
stratum cambium
and stratum
fibrosum
Blood vessel with Periosteum with
branches entering stratum cambium
Volkmann’s canal and stratum fibrosum
3.34 Section of compact bone from the diaphysis of a long bone (schematic).
Vet Histology.indb 85 16/07/2019 14:56