Page 54 - Rule Outs in Small Animal Medicine, Problem-oriented Assessment of Problems in Physical Examination and Clinical Pathology, 2nd Edition
P. 54
Internal Medicine Internal Medicine
Gastrointestinal tract Gastrointestinal tract
VetBooks.ir
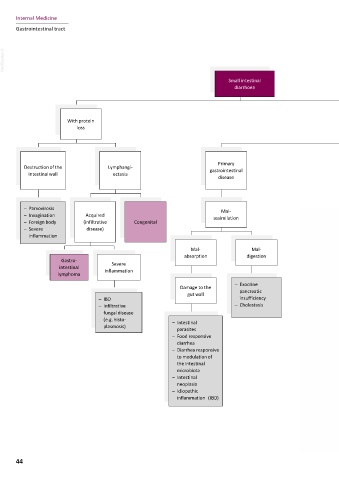
Small intestinal
diarrhoea
With protein Without protein
loss loss
Primary
Destruction of the Lymphangi- gastrointestinal Secondary to
intestinal wall ectasia systemic disease
disease
– Parvovirosis Mal- Destruction of
– Invagination Acquired assimilation Increased Changes in Inflammation the normal Cell damage due
– Foreign body (infiltrative Congenital intestinal motility mucosal spreading to the bacterial gut to systemic
– Severe disease) perfusion intestinal tract flora toxins
inflammation
Mal- Mal-
absorption digestion
Gastro- – Hyper- – Shock – Pancreatitis – Antibiotic – Uraemia
intestinal Severe thyroidism – Hypoadreno- – Peritonitis therapy – Chemo-
lymphoma inflammation corticism therapeutic
– Thrombosis agents
– Exocrine
Damage to the – Portal
gut wall pancreatic hypertension
– IBD insufficiency (e.g. liver
– Infiltrative – Cholestasis cirrhosis)
fungal disease
(e.g. histo- – Intestinal
plasmosis)
parasites
– Food responsive
diarrhea
– Diarrhea responsive
to modulation of
the intestinal
microbiota
– Intestinal
neoplasia
– Idiopathic
inflammation (IBD)
44 45