Page 70 - Rule Outs in Small Animal Medicine, Problem-oriented Assessment of Problems in Physical Examination and Clinical Pathology, 2nd Edition
P. 70
Internal Medicine Internal Medicine
Urinary tract Urinary tract
VetBooks.ir
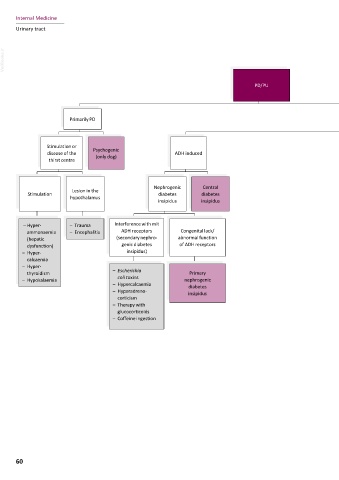
PD/PU
Primarily PD Primarily PU
Stimulation or Psychogenic Influence of Loss of nephron
disease of the (only dog) ADH induced osmotically active function
thirst centre particles
Nephrogenic Central
Lesion in the In renal medulla In urine too Chronic kidney Acute kidney
Stimulation diabetes diabetes
hypothalamus too little ... much ... disease injury
insipidus insipidus
– Hyper- – Trauma Interference with mit ... – Ischaemia
ammonaemia – Encephalitis ADH receptors Congenital lack/ osmotically ... glucose – Lepto-
(hepatic (secondary nephro- abnormal function ... sodium ... urea active ... sodium ... urea (glucosuria) spirosis
dysfunction) genic diabetes of ADH receptors therapy – Ingestion of
– Hyper- insipidus) toxins
calcaemia (e.g.
– Hyper- – Hypo- – Medullary – Mannitol – Hypo- – Post- – Diabetes ethylene
thyroidism – Escherichia Primary adreno- washout – Intravenous adreno- obstructive mellitus glycol,
– Hypokalaemia coli toxins nephrogenic corticism – Hepatic adminis- corticism diuresis – Fanconi raisins,
– Hypercalcaemia diabetes grapes)
– Hyperadreno- insipidus – Medullary dysfunction tration of (e.g. after syndrome – Pyelone-
corticism washout highly FLUTD) – Damage to phritis
– Therapy with – Sodium- concentrated – Chronic tubular
glucocorticoids deficient glucose kidney epithelium
– Coffeine ingestion diet solution disease (e.g. due to
(e.g. 10%) nephrotoxins)
60 61