Page 66 - Rule Outs in Small Animal Medicine, Problem-oriented Assessment of Problems in Physical Examination and Clinical Pathology, 2nd Edition
P. 66
Internal Medicine Internal Medicine
Gastrointestinal tract Gastrointestinal tract
Rubrik Rubrik
VetBooks.ir
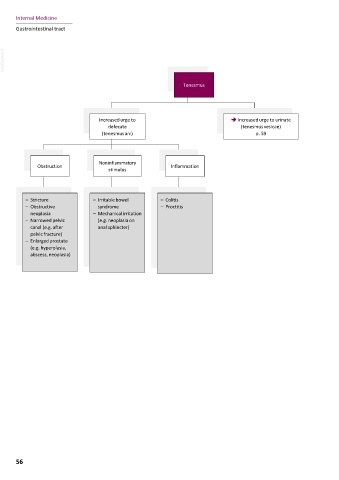
Tenesmus Hypersalivation
Swallowing Incomplete closure Increased saliva
Increased urge to â Increased urge to urinate disorders of mouth production
defecate (tenesmus vesicae)
(tenesmus ani) p. 59
Mechanical Neurological – Jaw Diseases of the Neuronal Lesion in the
obstruction disorder abnormality salivary gland stimuli oral cavity
Noninflammatory (e.g.
Obstruction Inflammation
stimulus luxation)
– Lip
– Foreign body – Crico- abnormality – Sialoadenitis – Nausea – Calicivirus
– Swelling pharyngeal – Trauma – Stimulation infection
– Stricture – Irritable bowel – Colitis – Neoplasia achalasia of the (cat)
– Obstructive syndrome – Proctitis – Rabies appetite – Chemical
neoplasia – Mechanical irritation – Tetanus center burns
– Narrowed pelvic (e.g. neoplasia on – Injury due to
canal (e.g. after anal sphincter) foreign body
pelvic fracture)
– Enlarged prostate
(e.g. hyperplasia,
abscess, neoplasia)
56 57