Page 73 - Rule Outs in Small Animal Medicine, Problem-oriented Assessment of Problems in Physical Examination and Clinical Pathology, 2nd Edition
P. 73
Internal Medicine Internal Medicine
Urinary tract Urinary tract
VetBooks.ir
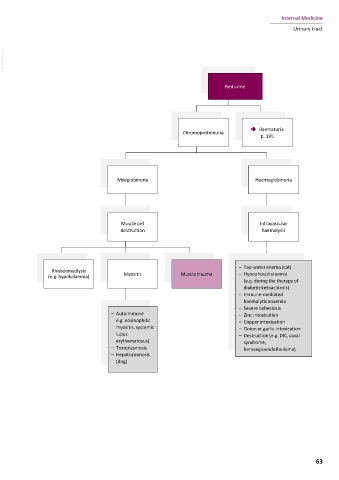
Red urine
Colourless urine Brown urine
Chromoproteinuria â Haematuria
p. 195
Urine not concentrated Bilirubinuria
Myoglobinuria Haemoglobinuria
Increased proportion of water Normal
in urine Hyperbilirubinaemia (+ to ++ in female dog,
+ to +++ in male dog)
Muscle cell Intravascular
destruction haemolysis
â PD/PU â Icterus – Tap-water enema (cat)
pp. 60–61
Rhabdomyolysis
pp. 14–15 (e.g. hypokalaemia) Myositis Muscle trauma – Hypophosphataemia
(e.g. during the therapy of
diabetic ketoacidosis)
– Immune-mediated
haemolytic anaemia
– Severe babesiosis
– Autoimmune – Zinc intoxication
e.g. eosinophilic – Copper intoxication
myositis, systemic – Onion or garlic intoxication
lupus – Destruction (e.g. DIC, caval
erythematosus) syndrome,
– Toxoplasmosis hemangioendothelioma)
– Hepatozoonosis
(dog)
62 63