Page 1062 - Clinical Small Animal Internal Medicine
P. 1062
1000 Section 9 Infectious Disease
and rarely cats that is often fatal. In the US, pythiosis Cytologic examination of smears, brushings or biopsies
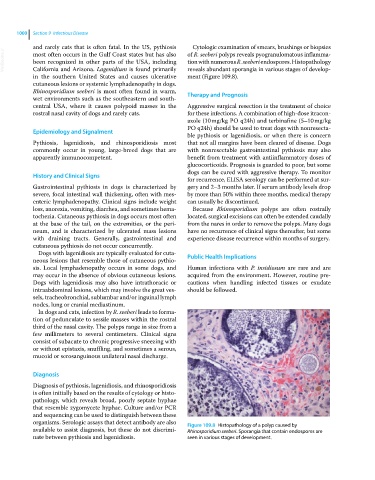
VetBooks.ir most often occurs in the Gulf Coast states but has also of R. seeberi polyps reveals pyogranulomatous inflamma
tion with numerous R. seeberi endospores. Histopathology
been recognized in other parts of the USA, including
California and Arizona. Lagenidium is found primarily
ment (Figure 109.8).
in the southern United States and causes ulcerative reveals abundant sporangia in various stages of develop
cutaneous lesions or systemic lymphadenopathy in dogs.
Rhinosporidium seeberi is most often found in warm, Therapy and Prognosis
wet environments such as the southeastern and south‐
central USA, where it causes polypoid masses in the Aggressive surgical resection is the treatment of choice
rostral nasal cavity of dogs and rarely cats. for these infections. A combination of high‐dose itracon
azole (10 mg/kg PO q24h) and terbinafine (5–10 mg/kg
PO q24h) should be used to treat dogs with nonresecta
Epidemiology and Signalment
ble pythiosis or lagenidiosis, or when there is concern
Pythiosis, lagenidiosis, and rhinosporidiosis most that not all margins have been cleared of disease. Dogs
commonly occur in young, large‐breed dogs that are with nonresectable gastrointestinal pythiosis may also
apparently immunocompetent. benefit from treatment with antiinflammatory doses of
glucocorticoids. Prognosis is guarded to poor, but some
dogs can be cured with aggressive therapy. To monitor
History and Clinical Signs
for recurrence, ELISA serology can be performed at sur
Gastrointestinal pythiosis in dogs is characterized by gery and 2–3 months later. If serum antibody levels drop
severe, focal intestinal wall thickening, often with mes by more than 50% within three months, medical therapy
enteric lymphadenopathy. Clinical signs include weight can usually be discontinued.
loss, anorexia, vomiting, diarrhea, and sometimes hema Because Rhinosporidium polyps are often rostrally
tochezia. Cutaneous pythiosis in dogs occurs most often located, surgical excisions can often be extended caudally
at the base of the tail, on the extremities, or the peri from the nares in order to remove the polyps. Many dogs
neum, and is characterized by ulcerated mass lesions have no recurrence of clinical signs thereafter, but some
with draining tracts. Generally, gastrointestinal and experience disease recurrence within months of surgery.
cutaneous pythiosis do not occur concurrently.
Dogs with lagenidiosis are typically evaluated for cuta
neous lesions that resemble those of cutaneous pythio Public Health Implications
sis. Local lymphadenopathy occurs in some dogs, and Human infections with P. insidiosum are rare and are
may occur in the absence of obvious cutaneous lesions. acquired from the environment. However, routine pre
Dogs with lagenidiosis may also have intrathoracic or cautions when handling infected tissues or exudate
intraabdominal lesions, which may involve the great ves should be followed.
sels, tracheobronchial, sublumbar and/or inguinal lymph
nodes, lung or cranial mediastinum.
In dogs and cats, infection by R. seeberi leads to forma
tion of pedunculate to sessile masses within the rostral
third of the nasal cavity. The polyps range in size from a
few millimeters to several centimeters. Clinical signs
consist of subacute to chronic progressive sneezing with
or without epistaxis, snuffling, and sometimes a serous,
mucoid or serosanguinous unilateral nasal discharge.
Diagnosis
Diagnosis of pythiosis, lagenidiosis, and rhinosporidiosis
is often initially based on the results of cytology or histo
pathology, which reveals broad, poorly septate hyphae
that resemble zygomycete hyphae. Culture and/or PCR
and sequencing can be used to distinguish between these
organisms. Serologic assays that detect antibody are also Figure 109.8 Histopathology of a polyp caused by
available to assist diagnosis, but these do not discrimi Rhinosporidium seeberi. Sporangia that contain endospores are
nate between pythiosis and lagenidiosis. seen in various stages of development.