Page 317 - Veterinary Immunology, 10th Edition
P. 317
VetBooks.ir MHC Molecules and Disease
Since the function of MHC molecules is to present antigens to the
cells of the immune system, MHC genes regulate immune
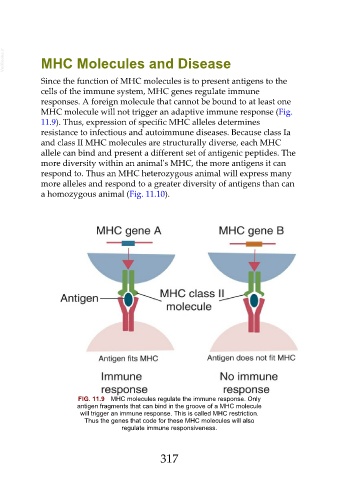
responses. A foreign molecule that cannot be bound to at least one
MHC molecule will not trigger an adaptive immune response (Fig.
11.9). Thus, expression of specific MHC alleles determines
resistance to infectious and autoimmune diseases. Because class Ia
and class II MHC molecules are structurally diverse, each MHC
allele can bind and present a different set of antigenic peptides. The
more diversity within an animal's MHC, the more antigens it can
respond to. Thus an MHC heterozygous animal will express many
more alleles and respond to a greater diversity of antigens than can
a homozygous animal (Fig. 11.10).
FIG. 11.9 MHC molecules regulate the immune response. Only
antigen fragments that can bind in the groove of a MHC molecule
will trigger an immune response. This is called MHC restriction.
Thus the genes that code for these MHC molecules will also
regulate immune responsiveness.
317