Page 332 - Veterinary Immunology, 10th Edition
P. 332
VetBooks.ir
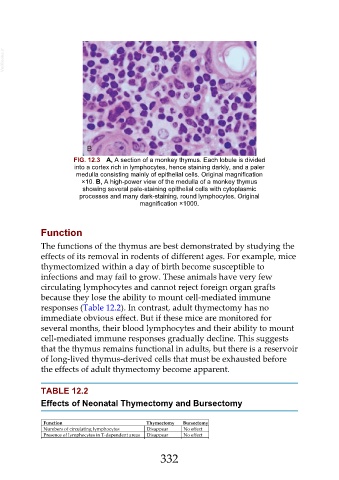
FIG. 12.3 A, A section of a monkey thymus. Each lobule is divided
into a cortex rich in lymphocytes, hence staining darkly, and a paler
medulla consisting mainly of epithelial cells. Original magnification
×10. B, A high-power view of the medulla of a monkey thymus
showing several pale-staining epithelial cells with cytoplasmic
processes and many dark-staining, round lymphocytes. Original
magnification ×1000.
Function
The functions of the thymus are best demonstrated by studying the
effects of its removal in rodents of different ages. For example, mice
thymectomized within a day of birth become susceptible to
infections and may fail to grow. These animals have very few
circulating lymphocytes and cannot reject foreign organ grafts
because they lose the ability to mount cell-mediated immune
responses (Table 12.2). In contrast, adult thymectomy has no
immediate obvious effect. But if these mice are monitored for
several months, their blood lymphocytes and their ability to mount
cell-mediated immune responses gradually decline. This suggests
that the thymus remains functional in adults, but there is a reservoir
of long-lived thymus-derived cells that must be exhausted before
the effects of adult thymectomy become apparent.
TABLE 12.2
Effects of Neonatal Thymectomy and Bursectomy
Function Thymectomy Bursectomy
Numbers of circulating lymphocytes Disappear No effect
Presence of lymphocytes in T-dependent areas Disappear No effect
332