Page 396 - Veterinary Immunology, 10th Edition
P. 396
structure, although they differ in size as a result of variations in
VetBooks.ir glycosylation. Thus the α chain is 43 to 49 kDa, the β chain is 38 to
44 kDa, the γ chain is 36 to 46 kDa, and the δ chain is 40 kDa. Each
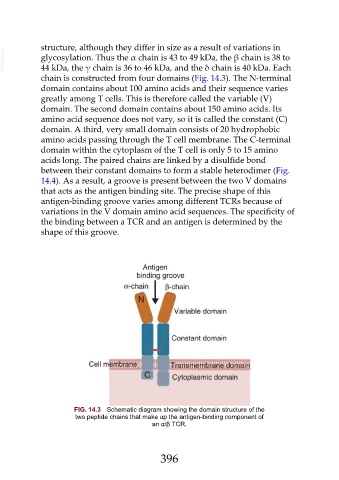
chain is constructed from four domains (Fig. 14.3). The N-terminal
domain contains about 100 amino acids and their sequence varies
greatly among T cells. This is therefore called the variable (V)
domain. The second domain contains about 150 amino acids. Its
amino acid sequence does not vary, so it is called the constant (C)
domain. A third, very small domain consists of 20 hydrophobic
amino acids passing through the T cell membrane. The C-terminal
domain within the cytoplasm of the T cell is only 5 to 15 amino
acids long. The paired chains are linked by a disulfide bond
between their constant domains to form a stable heterodimer (Fig.
14.4). As a result, a groove is present between the two V domains
that acts as the antigen binding site. The precise shape of this
antigen-binding groove varies among different TCRs because of
variations in the V domain amino acid sequences. The specificity of
the binding between a TCR and an antigen is determined by the
shape of this groove.
FIG. 14.3 Schematic diagram showing the domain structure of the
two peptide chains that make up the antigen-binding component of
an α/β TCR.
396