Page 397 - Veterinary Immunology, 10th Edition
P. 397
VetBooks.ir
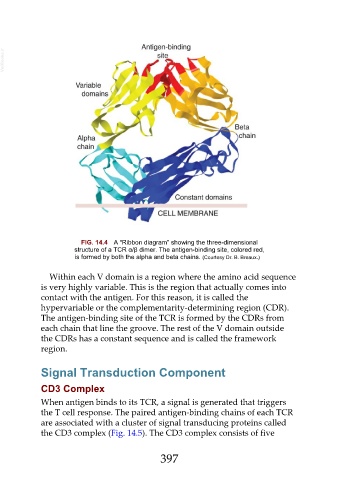
FIG. 14.4 A “Ribbon diagram” showing the three-dimensional
structure of a TCR α/β dimer. The antigen-binding site, colored red,
is formed by both the alpha and beta chains. (Courtesy Dr. B. Breaux.)
Within each V domain is a region where the amino acid sequence
is very highly variable. This is the region that actually comes into
contact with the antigen. For this reason, it is called the
hypervariable or the complementarity-determining region (CDR).
The antigen-binding site of the TCR is formed by the CDRs from
each chain that line the groove. The rest of the V domain outside
the CDRs has a constant sequence and is called the framework
region.
Signal Transduction Component
CD3 Complex
When antigen binds to its TCR, a signal is generated that triggers
the T cell response. The paired antigen-binding chains of each TCR
are associated with a cluster of signal transducing proteins called
the CD3 complex (Fig. 14.5). The CD3 complex consists of five
397