Page 406 - Veterinary Immunology, 10th Edition
P. 406
VetBooks.ir Signal Transduction
Once a TCR binds to antigen on a presenting cell and an
immunological synapse forms, the receptor signals to the T cell.
Several TCRs cluster so that the immunoreceptor tyrosine-based
activation motifs (ITAMs) on the CD3 chains can activate their
tyrosine kinases (Chapter 8). These form a signaling complex that
acts through calcineurin to activate NF-AT. It also activates the ras-
mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) pathway that triggers
AP-1 production and a protein kinase C-dependent pathway that
activates NF-κB. These three transcription factors activate multiple
cytokine genes (see Fig. 8.11). As a result, the T cells enter the cell
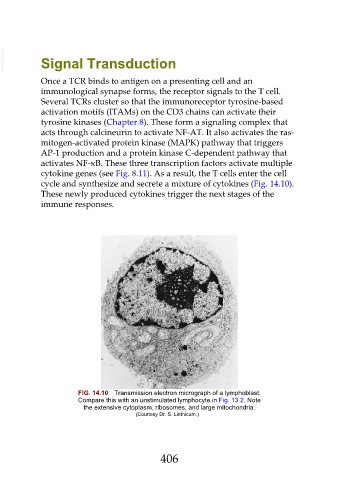
cycle and synthesize and secrete a mixture of cytokines (Fig. 14.10).
These newly produced cytokines trigger the next stages of the
immune responses.
FIG. 14.10 Transmission electron micrograph of a lymphoblast.
Compare this with an unstimulated lymphocyte in Fig. 13.2. Note
the extensive cytoplasm, ribosomes, and large mitochondria.
(Courtesy Dr. S. Linthicum.)
406