Page 496 - Veterinary Immunology, 10th Edition
P. 496
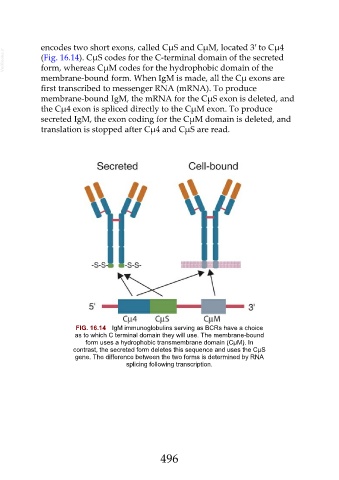
encodes two short exons, called CµS and CµM, located 3′ to Cµ4
VetBooks.ir (Fig. 16.14). CµS codes for the C-terminal domain of the secreted
form, whereas CµM codes for the hydrophobic domain of the
membrane-bound form. When IgM is made, all the Cµ exons are
first transcribed to messenger RNA (mRNA). To produce
membrane-bound IgM, the mRNA for the CµS exon is deleted, and
the Cµ4 exon is spliced directly to the CµM exon. To produce
secreted IgM, the exon coding for the CµM domain is deleted, and
translation is stopped after Cµ4 and CµS are read.
FIG. 16.14 IgM immunoglobulins serving as BCRs have a choice
as to which C terminal domain they will use. The membrane-bound
form uses a hydrophobic transmembrane domain (CµM). In
contrast, the secreted form deletes this sequence and uses the CµS
gene. The difference between the two forms is determined by RNA
splicing following transcription.
496