Page 565 - Veterinary Immunology, 10th Edition
P. 565
VetBooks.ir
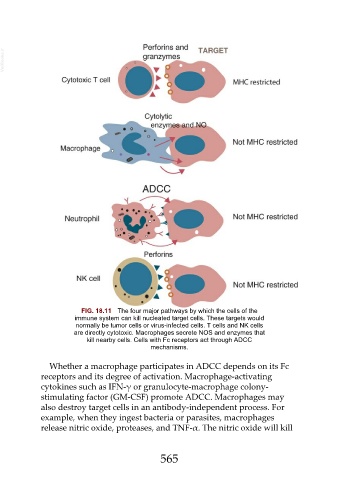
FIG. 18.11 The four major pathways by which the cells of the
immune system can kill nucleated target cells. These targets would
normally be tumor cells or virus-infected cells. T cells and NK cells
are directly cytotoxic. Macrophages secrete NOS and enzymes that
kill nearby cells. Cells with Fc receptors act through ADCC
mechanisms.
Whether a macrophage participates in ADCC depends on its Fc
receptors and its degree of activation. Macrophage-activating
cytokines such as IFN-γ or granulocyte-macrophage colony-
stimulating factor (GM-CSF) promote ADCC. Macrophages may
also destroy target cells in an antibody-independent process. For
example, when they ingest bacteria or parasites, macrophages
release nitric oxide, proteases, and TNF-α. The nitric oxide will kill
565