Page 593 - Veterinary Immunology, 10th Edition
P. 593
CD16 is a 38-kDa transmembrane protein linked to either the γ
VetBooks.ir chain of FcγRI (in macrophages) or to the zeta chain of CD3 (in NK
cells). When antibodies bind to target cells, the bound antibody
links to NK cell CD16, triggers cytotoxicity, and the target cells are
killed. NK cells can spontaneously release their CD16 so that the
NK cell can detach from an antibody-coated target after it has
delivered its lethal hit.
Effector Mechanisms
NK cell activities are regulated by cytokines and pathogen-
associated molecular patterns (PAMPs). For example, IL-2 and IL-4
enhance their cytotoxicity, whereas IL-3 enhances NK survival.
Although NK cells are active in the nonimmune animal, virus
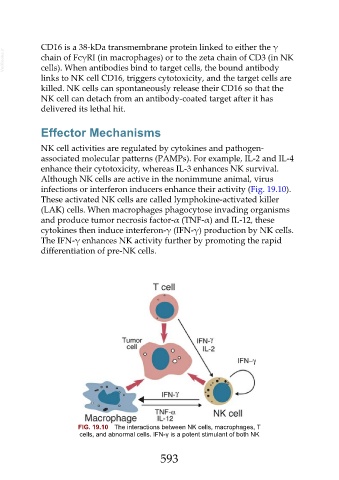
infections or interferon inducers enhance their activity (Fig. 19.10).
These activated NK cells are called lymphokine-activated killer
(LAK) cells. When macrophages phagocytose invading organisms
and produce tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α) and IL-12, these
cytokines then induce interferon-γ (IFN-γ) production by NK cells.
The IFN-γ enhances NK activity further by promoting the rapid
differentiation of pre-NK cells.
FIG. 19.10 The interactions between NK cells, macrophages, T
cells, and abnormal cells. IFN-γ is a potent stimulant of both NK
593