Page 137 - Manual of Equine Field Surgery
P. 137
Tooth Repulsion 133
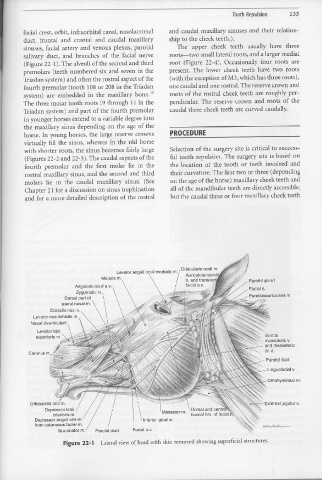
facial crest, orbit, infraorbital canal, nasolacrimal and caudal maxillary sinuses and their relation-
duct, frontal and cranial and caudal maxillary ship to the cheek teeth.).
sinuses, facial artery and venous plexus, parotid The upper cheek teeth usually have three
salivary duct, and branches of the facial nerve roots-two small lateral roots, and a larger medial
(Figure 22-1). The alveoli of the second and third root (Figure 22-4). Occasionally four roots are
premolars ( teeth numbered six and seven in the present. The lower cheek teeth have two roots
Triadan system) and often the rostral aspect of the ( with the exception of M3, which has three roots),
fourth premolar ( tooth 108 or 208 in the Triadan one caudal and one rostral. The reserve crown and
system) are embedded in the maxillary bone." roots of the rostral cheek teeth are roughly per-
The three molar tooth roots (9 through 11 in the pendicular. The reserve crown and roots of the
Triadan system) and part of the fourth premolar caudal three cheek teeth are curved caudally.
in younger horses extend to a variable degree into
the maxillary sinus depending 011 the age of the
horse. In young horses, the large reserve crowns PROCEDURE
virtually fill the sinus, whereas in the old horse
with shorter roots, the sinus becomes fairly large Selection of the surgery site is critical to success-
(Figures 22-2 and 22-3). The caudal aspects of the ful tooth repulsion. The surgery site is based on
fourth premolar and the first molar lie in the the location of the tooth or teeth involved and
rostral maxillary sinus, and the second and third their curvature. The first two or three ( depending
molars lie in the caudal maxillary sinus. (See on the age of the horse) maxillary cheek teeth and
Chapter 21 for a discussion on sinus trephination all of the mandibular teeth are directly accessible,
and for a more detailed description of the rostral but the caudal three or four maxillary cheek teeth
Orbicularis oculi m.
Levator anguli oculi medialis m.
Aurlculotempora
Malaris m. n. and transver Parotid gland
Angularis oculi a.v. facial a.v. Facial n.
Zygomatic m.
Dorsal part of Parotidoauricularis m.
lateral nasal m.
Dorsalis nasi v.
Levator nasolabialis m.
Nasal diverticulum
Levator labii
superioris m.
Orbicularis oris m.
Depressor labii Masseter m.
inferioris m.
Depressor anguli oris m. Inferior labial a.
from cutaneous faciei m.
Buccinator m. Parotid duct Facial a.v.
Figure 22-1 Lateral view of head with skin removed showing superficial structures,