Page 32 - Manual of Equine Field Surgery
P. 32
r
28 PRESURGICAL PREPARATION AND ASSESSMENT
I
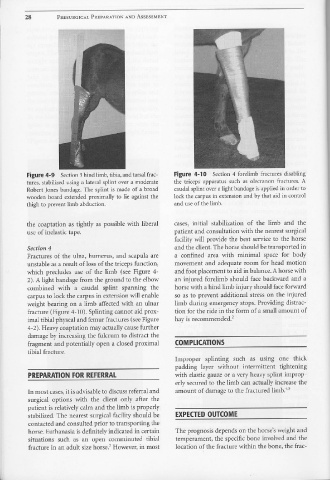
Figure 4-9 Section 3 hind limb, tibia, and tarsal frac- Figure 4-10 Section 4 forelimb fractures disabling
tures, stabilized using a lateral splint over a moderate the triceps apparatus such as olecranon fractures. A
Robert Jones bandage. The splint is made of a broad caudal splint over a light bandage is applied in order to
wooden board extended proximally to lie against the lock the carpus in extension and by that aid in control
thigh to prevent limb abduction. and use of the limb.
the coaptation as tightly as possible with liberal cases, initial stabilization of the limb and the
use of inelastic tape. patient and consultation with the nearest surgical
facility will provide the best service to the horse
Section 4 and the client. The horse should be transported in
Fractures of the ulna, humerus, and scapula are a confined area with minimal space for body
unstable as a result of loss of the triceps function, movement and adequate room for head motion
which precludes use of the limb ( see Figure 4- a11d foot placement to aid in balance. A horse with
2). A light bandage from the ground to the elbow an injured forelimb should face backward and a
combined with a caudal splint spanning the horse with a hind limb injury should face forward
carpus to lock the carpus in extension will enable so as to prevent additional stress on the injured
weight bearing on a limb affected with an ulnar limb during emergency stops. Providing distrac-
fracture (Figure 4-10). Splinting cannot aid prox - tion for the ride in the form of a small amount of
imal tibial physeal and femur fractures ( see Figure hay is recommended. 2
4-2). Heavy coaptation may actually cause further
damage by increasing the fulcrum to distract the
fragment and potentially open a closed proximal COMPLICATIONS
tibial fracture.
Improper splinting such as using one thick
padding layer without intermittent tightening
PREPARATION FOR REFERRAL with elastic gauze or a very heavy splint improp-
erly secured to the limb can actually increase the
In most cases, it is advisable to discuss referral and amount of damage to the fractured limb.v"
surgical options with the client only after the
patient is relatively calm and the limb is properly
stabilized. The nearest surgical facility should be EXPECTED OUTCOME
contacted and consulted prior to transporting the
horse. Euthanasia is definitely indicated in certain The prognosis depends on the horse's weight and
situations such as an open comminuted tibial temperament, the specific bone involved and the
fracture in an adult size horse.5 However, in most location of the fracture within the bone, the frac-
'