Page 241 - Veterinary Histology of Domestic Mammals and Birds, 5th Edition
P. 241
Digestive system (apparatus digestorius) 223
VetBooks.ir
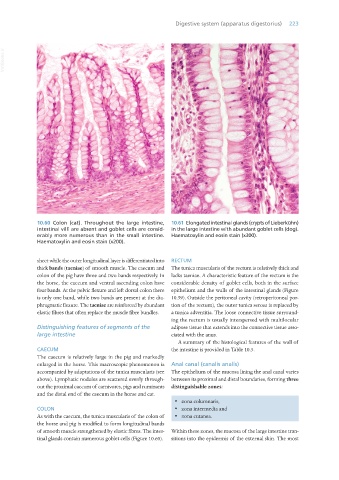
10.60 Colon (cat). Throughout the large intestine, 10.61 Elongated intestinal glands (crypts of Lieberkühn)
intestinal villi are absent and goblet cells are consid- in the large intestine with abundant goblet cells (dog).
erably more numerous than in the small intestine. Haematoxylin and eosin stain (x300).
Haematoxylin and eosin stain (x200).
sheet while the outer longitudinal layer is differentiated into RECTUM
thick bands (taeniae) of smooth muscle. The caecum and The tunica muscularis of the rectum is relatively thick and
colon of the pig have three and two bands respectively. In lacks taeniae. A characteristic feature of the rectum is the
the horse, the caecum and ventral ascending colon have considerable density of goblet cells, both in the surface
four bands. At the pelvic flexure and left dorsal colon there epithelium and the walls of the intestinal glands (Figure
is only one band, while two bands are present at the dia- 10.59). Outside the peritoneal cavity (retroperitoneal por-
phragmatic flexure. The taeniae are reinforced by abundant tion of the rectum), the outer tunica serosa is replaced by
elastic fibres that often replace the muscle fibre bundles. a tunica adventitia. The loose connective tissue surround-
ing the rectum is usually interspersed with multilocular
Distinguishing features of segments of the adipose tissue that extends into the connective tissue asso-
large intestine ciated with the anus.
A summary of the histological features of the wall of
CAECUM the intestine is provided in Table 10.5.
The caecum is relatively large in the pig and markedly
enlarged in the horse. This macroscopic phenomenon is Anal canal (canalis analis)
accompanied by adaptations of the tunica muscularis (see The epithelium of the mucosa lining the anal canal varies
above). Lymphatic nodules are scattered evenly through- between its proximal and distal boundaries, forming three
out the proximal caecum of carnivores, pigs and ruminants distinguishable zones:
and the distal end of the caecum in the horse and cat.
· zona columnaris,
COLON · zona intermedia and
As with the caecum, the tunica muscularis of the colon of · zona cutanea.
the horse and pig is modified to form longitudinal bands
of smooth muscle strengthened by elastic fibres. The intes- Within these zones, the mucosa of the large intestine tran-
tinal glands contain numerous goblet cells (Figure 10.60). sitions into the epidermis of the external skin. The most
Vet Histology.indb 223 16/07/2019 15:01