Page 242 - Veterinary Histology of Domestic Mammals and Birds, 5th Edition
P. 242
224 Veterinary Histology of Domestic Mammals and Birds
proximal segment of the canal (zona columnaris) com- modification of steroids. In carnivores, paired anal sacs
VetBooks.ir mences at the anorectal line. Here the glandular mucosa (sinus paranales) lined with stratified squamous epithe-
of the rectum (lined with simple columnar epithelium) lium are present ventrolateral to the anal canal.
abruptly changes into the non-glandular mucosa of the
Located in the wall of the anal sacs are the glands of
anal canal (lined with stratified squamous epithelium). The the anal sacs (glandulae sinus paranales) These apocrine
zona columnaris is followed by the narrow zona interme- modified sweat glands function as scent glands. In cats, the
dia. From its distal boundary (the anocutaneous line), the anal sacs also contain sebaceous glands.
zona intermedia is continued by the zona cutanea which
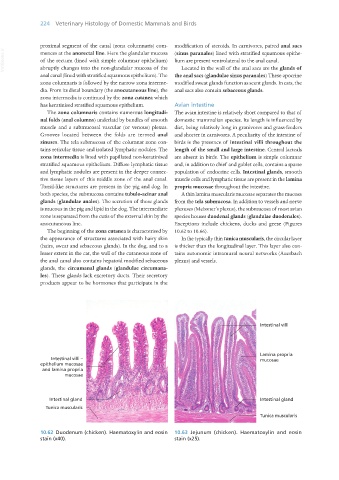
has keratinised stratified squamous epithelium. Avian intestine
The zona columnaris contains numerous longitudi- The avian intestine is relatively short compared to that of
nal folds (anal columns) underlaid by bundles of smooth domestic mammalian species. Its length is influenced by
muscle and a submucosal vascular (or venous) plexus. diet, being relatively long in granivores and grass-feeders
Grooves located between the folds are termed anal and shorter in carnivores. A peculiarity of the intestine of
sinuses. The tela submucosa of the columnar zone con- birds is the presence of intestinal villi throughout the
tains reticular tissue and isolated lymphatic nodules. The length of the small and large intestine. Central lacteals
zona intermedia is lined with papillated non-keratinised are absent in birds. The epithelium is simple columnar
stratified squamous epithelium. Diffuse lymphatic tissue and, in addition to chief and goblet cells, contains a sparse
and lymphatic nodules are present in the deeper connec- population of endocrine cells. Intestinal glands, smooth
tive tissue layers of this middle zone of the anal canal. muscle cells and lymphatic tissue are present in the lamina
Tonsil-like structures are present in the pig and dog. In propria mucosae throughout the intestine.
both species, the submucosa contains tubulo-acinar anal A thin lamina muscularis mucosae separates the mucosa
glands (glandulae anales). The secretion of these glands from the tela submucosa. In addition to vessels and nerve
is mucous in the pig and lipid in the dog. The intermediate plexuses (Meissner’s plexus), the submucosa of most avian
zone is separated from the cutis of the external skin by the species houses duodenal glands (glandulae duodenales).
anocutaneous line. Exceptions include chickens, ducks and geese (Figures
The beginning of the zona cutanea is characterised by 10.62 to 10.66).
the appearance of structures associated with hairy skin In the typically thin tunica muscularis, the circular layer
(hairs, sweat and sebaceous glands). In the dog, and to a is thicker than the longitudinal layer. This layer also con-
lesser extent in the cat, the wall of the cutaneous zone of tains autonomic intramural neural networks (Auerbach
the anal canal also contains hepatoid modified sebaceous plexus) and vessels.
glands, the circumanal glands (glandulae circumana-
les). These glands lack excretory ducts. Their secretory
products appear to be hormones that participate in the
Intestinal villi –
epithelium mucosae
and lamina propria
mucosae
Intestinal gland
Tunica muscularis
10.62 Duodenum (chicken). Haematoxylin and eosin 10.63 Jejunum (chicken). Haematoxylin and eosin
stain (x40). stain (x25).
Vet Histology.indb 224 16/07/2019 15:01