Page 307 - Veterinary Histology of Domestic Mammals and Birds, 5th Edition
P. 307
Male reproductive system (organa genitalia masculina) 289
Particularly in segment 1 of the epididymal duct, pro- high capacity for resorption of fluid. Ninety percent
VetBooks.ir teins are released by the apocrine mode for maturation of the luminal fluid is absorbed in the ductuli efferentes
of spermatozoa. In segment 6, the environment facilitates and the initial portion of the epididymal duct. Androgen-
binding proteins and inhibin are also reabsorbed in the
survival of spermatozoa prior to ejaculation.
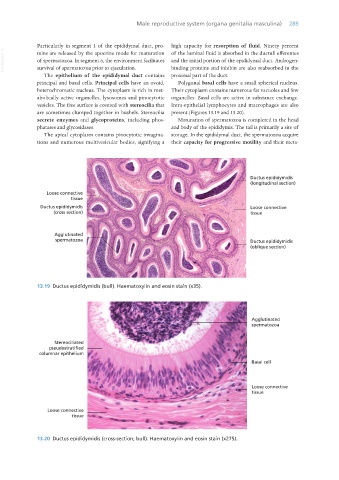
The epithelium of the epididymal duct contains proximal part of the duct.
principal and basal cells. Principal cells have an ovoid, Polygonal basal cells have a small spherical nucleus.
heterochromatic nucleus. The cytoplasm is rich in met- Their cytoplasm contains numerous fat vacuoles and few
abolically active organelles, lysosomes and pinocytotic organelles. Basal cells are active in substance exchange.
vesicles. The free surface is covered with stereocilia that Intra-epithelial lymphocytes and macrophages are also
are sometimes clumped together in bushels. Stereocilia present (Figures 13.19 and 13.20).
secrete enzymes and glycoproteins, including phos- Maturation of spermatozoa is completed in the head
phatases and glycosidases. and body of the epididymis. The tail is primarily a site of
The apical cytoplasm contains pinocytotic invagina- storage. In the epididymal duct, the spermatozoa acquire
tions and numerous multivesicular bodies, signifying a their capacity for progressive motility and their meta-
13.19 Ductus epididymidis (bull). Haematoxylin and eosin stain (x35).
13.20 Ductus epididymidis (cross-section; bull). Haematoxylin and eosin stain (x275).
Vet Histology.indb 289 16/07/2019 15:04