Page 14 - Rapid Review of ECG Interpretation in Small Animal Practice, 2nd Edition
P. 14
Section 1
VetBooks.ir PRINCIPLES OF
ELECTROCARDIOGRAPHY
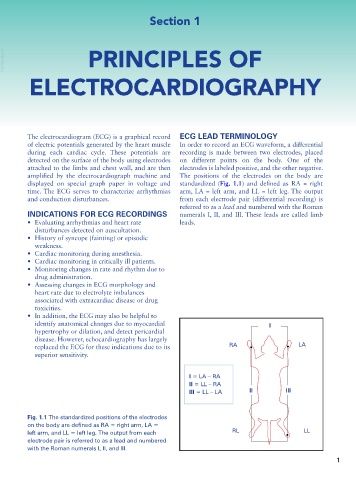
The electrocardiogram (ECG) is a graphical record ECG LEAD TERMINOLOGY
of electric potentials generated by the heart muscle In order to record an ECG waveform, a differential
during each cardiac cycle. These potentials are recording is made between two electrodes, placed
detected on the surface of the body using electrodes on different points on the body. One of the
attached to the limbs and chest wall, and are then electrodes is labeled positive, and the other negative.
amplified by the electrocardiograph machine and The positions of the electrodes on the body are
displayed on special graph paper in voltage and standardized (Fig. 1.1) and defined as RA = right
time. The ECG serves to characterize arrhythmias arm, LA = left arm, and LL = left leg. The output
and conduction disturbances. from each electrode pair (differential recording) is
referred to as a lead and numbered with the Roman
INDICATIONS FOR ECG RECORDINGS numerals I, II, and III. These leads are called limb
• Evaluating arrhythmias and heart rate leads.
disturbances detected on auscultation.
• History of syncope (fainting) or episodic
weakness.
• Cardiac monitoring during anesthesia.
• Cardiac monitoring in critically ill patients.
• Monitoring changes in rate and rhythm due to
drug administration.
• Assessing changes in ECG morphology and
heart rate due to electrolyte imbalances
associated with extracardiac disease or drug
toxicities.
• In addition, the ECG may also be helpful to
identify anatomical changes due to myocardial I
hypertrophy or dilation, and detect pericardial
disease. However, echocardiography has largely
replaced the ECG for these indications due to its RA LA
superior sensitivity.
I = LA – RA
II = LL – RA
III = LL – LA II III
Fig. 1.1 The standardized positions of the electrodes
on the body are defined as RA = right arm, LA =
left arm, and LL = left leg. The output from each RL LL
electrode pair is referred to as a lead and numbered
with the Roman numerals I, II, and III.
1