Page 18 - Rapid Review of ECG Interpretation in Small Animal Practice, 2nd Edition
P. 18
Principles of Electrocardiography
The actual action potential generated by the SA depolarize the right and left ventricles, respectively.
The left branch further divides into the anterior and
nodal cells (pacemaker potentials) are too small to be
VetBooks.ir seen on the surface ECG. However, as the activation posterior fascicule. Once the large muscle mass of
the ventricles is excited, a large deflection is seen
wavefront encounters the mass of atrial myocardium,
the initiation of electrical activity is observed on on the body surface, called the QRS complex. This
the body surface. Thus, the first ECG wave of the large wave can have several components. In lead
cardiac cycle is called the P wave and represents II, there may be an initial downward deflection,
activation of the atria. Atrial repolarization is rarely called the Q wave, followed by a dominant upward
appreciated on the ECG, as it occurs simultaneously deflection called the R wave. There may also be a
with ventricular depolarization and is thus hidden in terminal downward deflection, called the S wave.
the QRS complex. The polarity and actual presence of these three
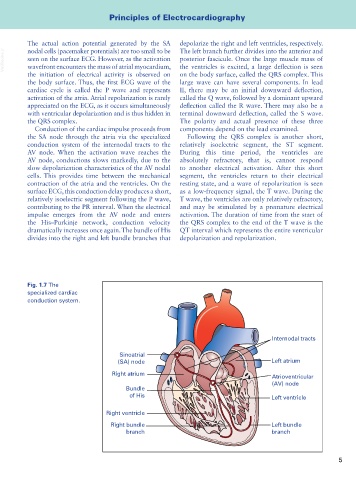
Conduction of the cardiac impulse proceeds from components depend on the lead examined.
the SA node through the atria via the specialized Following the QRS complex is another short,
conduction system of the internodal tracts to the relatively isoelectric segment, the ST segment.
AV node. When the activation wave reaches the During this time period, the ventricles are
AV node, conductions slows markedly, due to the absolutely refractory, that is, cannot respond
slow depolarization characteristics of the AV nodal to another electrical activation. After this short
cells. This provides time between the mechanical segment, the ventricles return to their electrical
contraction of the atria and the ventricles. On the resting state, and a wave of repolarization is seen
surface ECG, this conduction delay produces a short, as a low-frequency signal, the T wave. During the
relatively isoelectric segment following the P wave, T wave, the ventricles are only relatively refractory,
contributing to the PR interval. When the electrical and may be stimulated by a premature electrical
impulse emerges from the AV node and enters activation. The duration of time from the start of
the His–Purkinje network, conduction velocity the QRS complex to the end of the T wave is the
dramatically increases once again. The bundle of His QT interval which represents the entire ventricular
divides into the right and left bundle branches that depolarization and repolarization.
Fig. 1.7 The
specialized cardiac
conduction system.
Internodal tracts
Sinoatrial
(SA) node Left atrium
Right atrium Atrioventricular
(AV) node
Bundle
of His Left ventricle
Right ventricle
Right bundle Left bundle
branch branch
5