Page 70 - Poultry-Punch April 2020 edition
P. 70
POULTRY PUNCH ARTICLE
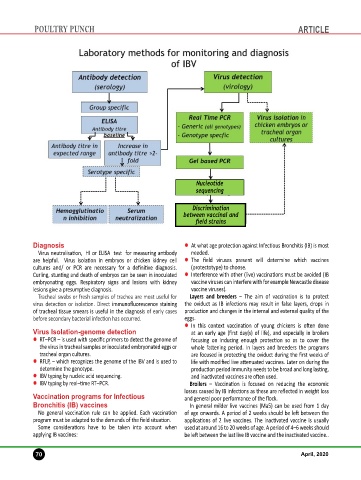
Nucleotide
sequencing
Discrimination
between vaccinal and
field strains
Diagnosis l At what age protection against Infectious Bronchitis (IB) is most
Virus neutralisation, HI or ELISA test for measuring antibody needed.
are helpful. Virus isolation in embryos or chicken kidney cell l The field viruses present will determine which vaccines
cultures and/ or PCR are necessary for a definitive diagnosis. (protectotype) to choose.
Curling, stunting and death of embryos can be seen in inoculated l Interference with other (live) vaccinations must be avoided (IB
embryonating eggs. Respiratory signs and lesions with kidney vaccine viruses can interfere with for example Newcastle disease
lesions give a presumptive diagnosis. vaccine viruses).
Tracheal swabs or fresh samples of trachea are most useful for Layers and breeders – The aim of vaccination is to protect
virus detection or isolation. Direct immunofluorescence staining the oviduct as IB infections may result in false layers, drops in
of tracheal tissue smears is useful in the diagnosis of early cases production and changes in the internal and external quality of the
before secondary bacterial infection has occurred. eggs.
l In this context vaccination of young chickens is often done
Virus Isolation-genome detection at an early age (first day(s) of life), and especially in broilers
l RT–PCR – is used with specific primers to detect the genome of focusing on inducing enough protection so as to cover the
the virus in tracheal samples or inoculated embryonated eggs or whole fattening period. In layers and breeders the programs
tracheal organ cultures. are focused in protecting the oviduct during the first weeks of
l RFLP, – which recognizes the genome of the IBV and is used to life with modified live attenuated vaccines. Later on during the
determine the genotype. production period immunity needs to be broad and long lasting,
l IBV typing by nucleic acid sequencing. and inactivated vaccines are often used.
l IBV typing by real–time RT–PCR. Broilers – Vaccination is focused on reducing the economic
losses caused by IB infections as these are reflected in weight loss
Vaccination programs for Infectious and general poor performance of the flock.
Bronchitis (IB) vaccines In general milder live vaccines (Ma5) can be used from 1 day
No general vaccination rule can be applied. Each vaccination of age onwards. A period of 2 weeks should be left between the
program must be adapted to the demands of the field situation. applications of 2 live vaccines. The inactivated vaccine is usually
Some considerations have to be taken into account when used at around 16 to 20 weeks of age. A period of 4–6 weeks should
applying IB vaccines: be left between the last live IB vaccine and the inactivated vaccine..
70 April, 2020