Page 17 - GP fall 2023
P. 17
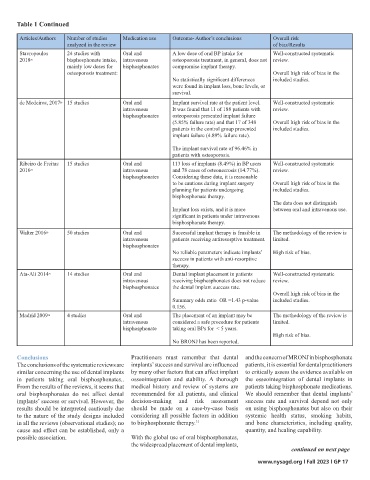
Table 1 Table 1 Continued
Articles/Authors Number of studies Medication use Outcome- Author’s conclusions Overall risk Articles/Authors Number of studies Medication use Outcome- Author’s conclusions Overall risk
analyzed in the review of bias/Results analyzed in the review of bias/Results
Lemos 2023 19 12 studies Oral and No difference in implant survival between Well-constructed systematic Stavropoulos 24 studies with Oral and A low dose of oral BP intake for Well-constructed systematic
intravenous patients with and without osteoporosis review. 2018 25 bisphosphonate intake, intravenous osteoporosis treatment, in general, does not review.
bisphosphonates OR 1.78 95% confidence interval (CI) Overall high risk of bias in the mainly low doses for bisphosphonates compromise implant therapy.
0.86-3.70 p-value: 0.12. included studies. osteoporosis treatment: Overall high risk of bias in the
No statistically significant differences included studies.
Dental implants are a viable treatment The data does not distinguish were found in implant loss, bone levels, or
option for rehabilitating patients with between oral and intravenous use. survival.
osteoporosis. de Medeiros, 2017 26 15 studies Oral and Implant survival rate at the patient level. Well-constructed systematic
Rebelo 2023 20 14 studies Oral and A high mean for failure- rate of implant Well-constructed systematic intravenous It was found that 11 of 188 patients with review.
intravenous osseointegration (49.96%) was found, review. bisphosphonates osteoporosis presented implant failure
bisphosphonates regardless of the type of BPs used. The Overall high risk of bias in the (5.85% failure rate) and that 17 of 348 Overall high risk of bias in the
failure rate was lower in patients using included studies. patients in the control group presented included studies.
second-generation BPs (Alendronate and implant failure (4.89% failure rate).
Pamidronate). The data does not distinguish
between oral and intravenous use. The implant survival rate of 96.46% in
patients with osteoporosis.
Sher, 2021 21 28 studies reporting on Oral and No substantial differences were observed Well-constructed systematic
bisphosphonates (BPs) intravenous between cases/controls, with an implant review. Ribeiro de Freitas 15 studies Oral and 113 loss of implants (8.49%) in BP users Well-constructed systematic
bisphosphonates. success rate ranging from Overall high risk of bias in the 2016 27 intravenous and 78 cases of osteonecrosis (14.77%). review.
92.9% to 100% for cases and 95.5% to included studies. bisphosphonates Considering these data, it is reasonable
100% for the controls. to be cautious during implant surgery Overall high risk of bias in the
The data does not distinguish planning for patients undergoing included studies.
Combining the included studies, between oral and intravenous use. bisphosphonate therapy.
the overall implant failure rate was The data does not distinguish
2.8% (patients taking bisphosphonates) Implant loss exists, and it is more between oral and intravenous use.
for cases and 2.1% for controls (not taking significant in patients under intravenous
bisphosphonates). bisphosphonate therapy.
Walter 2016 28 50 studies Oral and Successful implant therapy is feasible in The methodology of the review is
Implant losses were more likely to occur in intravenous patients receiving antiresorptive treatment. limited.
the posterior maxillary region and shortly bisphosphonates
after placement. No reliable parameters indicate implants’ High risk of bias.
success in patients with anti-resorptive
The follow-up period after therapy.
implant placement ranged from
0.3 to 12.2 years. Ata-Ali 2014 29 14 studies Oral and Dental implant placement in patients Well-constructed systematic
intravenous receiving bisphosphonates does not reduce review.
A risk of MRONJ developing after implant bisphosphonates the dental implant success rate.
placement in patients with a history of Overall high risk of bias in the
bisphosphonates. Summary odds ratio OR =1.43 p-value included studies.
0.156.
Chappuis, 2018 22 Of the 17 studies, 7 Oral and The usage of oral BPs for the treatment Well-constructed systematic
focused on BP use intravenous of osteoporosis did not yield significance review. Madrid 2009 30 4 studies Oral and The placement of an implant may be The methodology of the review is
and implant failure/ bisphosphonates when analyzing their impact on implant intravenous considered a safe procedure for patients limited.
success. failure or survival. Overall high risk of bias in the bisphosphonate taking oral BPs for < 5 years.
included studies High risk of bias.
Oral BP did not show statistical No BRONJ has been reported.
significance results.
Gelazious 2018 23 9 studies Oral and No significant differences in terms of the Well-constructed review. Conclusions Practitioners must remember that dental and the concern of MRONJ in bisphosphonate
intravenous success of implant placement. The conclusions of the systematic reviews are implants’ success and survival are influenced patients, it is essential for dental practitioners
bisphosphonates Overall high risk of bias in the similar concerning the use of dental implants by many other factors that can affect implant to critically assess the evidence available on
For patients with oral BP therapy, included studies. in patients taking oral bisphosphonates.. osseointegration and stability. A thorough the osseointegration of dental implants in
97% of dental implant success. From the results of the reviews, it seems that medical history and review of systems are patients taking bisphosphonate medications.
Schmitt 2018 24 18 studies Oral and Implant survival rate ranged from 92.86% Well-constructed systematic oral bisphosphonates do not affect dental recommended for all patients, and clinical We should remember that dental implants’
intravenous to 100%. review. implants’ success or survival. However, the decision-making and risk assessment success rate and survival depend not only
bisphosphonates results should be interpreted cautiously due should be made on a case-by-case basis on using bisphosphonates but also on their
Within the limits of this review, implant Overall high risk of bias in the to the nature of the study designs included considering all possible factors in addition systemic health status, smoking habits,
treatment seems to be a valuable approach. included studies. in all the reviews (observational studies); no to bisphosphonate therapy. 31 and bone characteristics, including quality,
cause and effect can be established, only a quantity, and healing capability.
Limitations for patients taking BP’s due to possible association. With the global use of oral bisphosphonates,
a malignant disease. the widespread placement of dental implants,
continued on next page
www.nysagd.org l Fall 2023 l GP 17