Page 4 - Viscosity measurement and prediction of gasified and synthesized coal slag melts
P. 4
Arman et al. / Fuel 200 (2017) 521–528 523
(T L ), proportions of solids, and mineral formation for synthesized and with 2 mm in diameter. The crucible and spindle used were
slags. The hot thermocouple (HTC) method [18] was used to deter- made from Pt–30wt%Rh. In order to confirm the accuracy and
mine the temperature of homogenous melting state for complex, the reproducibility of viscosity values for slag melts, the viscome-
coal ash slags. Table 1 indicates the liquidus temperatures T L of ter was calibrated at room temperature (25 °C) using Brookfield
synthesized slags. standard silicone fluids with four types of known viscosities
The HTC method [18] is an established experimental procedure (0.01, 0.502, 4.850, and 29.44 Pa s). The viscometer was calibrated
combined the Pt/Pt–13%Rh thermocouple, a stereoscopic micro- two or three times with different speeds of rotation cylinder, and
scope, camera and PC. The monitor of PC displays experimental the measured deviation from the mean was within 1.04%. The
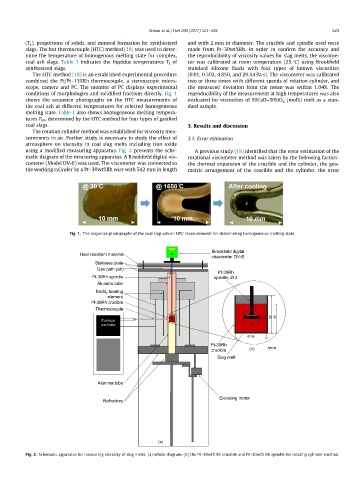
conditions of morphologies and solidified fractions directly. Fig. 1 reproducibility of the measurement at high temperatures was also
shows the sequence photographs on the HTC measurements of evaluated for viscosities of 50CaO–50SiO 2 (mol%) melt as a stan-
the coal ash at different temperatures for selected homogeneous dard sample.
melting state. Table 1 also shows homogeneous melting tempera-
tures T hm determined by the HTC method for four types of gasified
coal slags. 3. Results and discussion
The rotation cylinder method was established for viscosity mea-
surements in air. Further study is necessary to study the effect of 3.1. Error estimation
atmosphere on viscosity in coal slag melts including iron oxide
using a modified measuring apparatus. Fig. 2 presents the sche- A previous study [19] identified that the error estimation of the
matic diagram of the measuring apparatus. A Brookfield digital vis- rotational viscometer method was taken by the following factors:
cometer (Model DV-E) was used. The viscometer was connected to the thermal expansion of the crucible and the cylinder, the geo-
the working cylinder by a Pt–30wt%Rh wire with 542 mm in length metric arrangement of the crucible and the cylinder, the error
Fig. 1. The sequence photographs of the coal slag-ash on HTC measurements for determining homogeneous melting state.
Fig. 2. Schematic apparatus for measuring viscosity of slag melts: (a) whole diagram, (b) the Pt–30wt% Rh crucible and Pt–30wt% Rh spindle for rotating cylinder method.