Page 133 - MHF-FeedingMinds-final.indd
P. 133
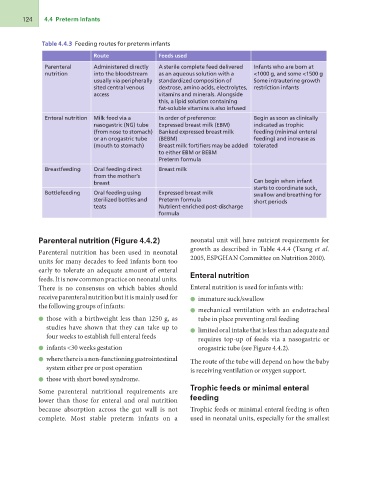
124 4.4 Preterm Infants
Table 4.4.3 Feeding routes for preterm infants
Route Feeds used
Parenteral Administered directly A sterile complete feed delivered Infants who are born at
nutrition into the bloodstream as an aqueous solution with a <1000 g, and some <1500 g
usually via peripherally standardized composition of Some intrauterine growth
Enteral nutrition sited central venous dextrose, amino acids, electrolytes, restriction infants
access vitamins and minerals. Alongside
Breastfeeding this, a lipid solution containing Begin as soon as clinically
Bottlefeeding Milk feed via a fat-soluble vitamins is also infused indicated as trophic
nasogastric (NG) tube feeding (minimal enteral
(from nose to stomach) In order of preference: feeding) and increase as
or an orogastric tube Expressed breast milk (EBM) tolerated
(mouth to stomach) Banked expressed breast milk
(BEBM) Can begin when infant
Oral feeding direct Breast milk fortifiers may be added starts to coordinate suck,
from the mother’s to either EBM or BEBM swallow and breathing for
breast Preterm formula short periods
Oral feeding using
sterilized bottles and Breast milk
teats
Expressed breast milk
Preterm formula
Nutrient-enriched post-discharge
formula
Parenteral nutrition (Figure 4.4.2) neonatal unit will have nutrient requirements for
growth as described in Table 4.4.4 (Tsang et al.
Parenteral nutrition has been used in neonatal 2005, ESPGHAN Committee on Nutrition 2010).
units for many decades to feed infants born too
early to tolerate an adequate amount of enteral Enteral nutrition
feeds. It is now common practice on neonatal units.
There is no consensus on which babies should Enteral nutrition is used for infants with:
receive parenteral nutrition but it is mainly used for
the following groups of infants: ●● immature suck/swallow
●● mechanical ventilation with an endotracheal
●● those with a birthweight less than 1250 g, as
studies have shown that they can take up to tube in place preventing oral feeding
four weeks to establish full enteral feeds ●● limited oral intake that is less than adequate and
●● infants <30 weeks gestation requires top-up of feeds via a nasogastric or
orogastric tube (see Figure 4.4.2).
●● where there is a non-functioning gastrointestinal
system either pre or post operation The route of the tube will depend on how the baby
is receiving ventilation or oxygen support.
●● those with short bowel syndrome.
Trophic feeds or minimal enteral
Some parenteral nutritional requirements are feeding
lower than those for enteral and oral nutrition
because absorption across the gut wall is not Trophic feeds or minimal enteral feeding is often
complete. Most stable preterm infants on a used in neonatal units, especially for the smallest