Page 299 - ABCTE Study Guide_Neat
P. 299
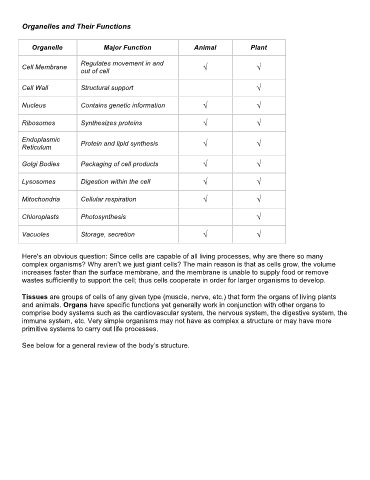
Organelles and Their Functions
Organelle Major Function Animal Plant
Regulates movement in and
Cell Membrane √ √
out of cell
Cell Wall Structural support √
Nucleus Contains genetic information √ √
Ribosomes Synthesizes proteins √ √
Endoplasmic Protein and lipid synthesis
Reticulum √ √
Golgi Bodies Packaging of cell products √ √
Lysosomes Digestion within the cell √ √
Mitochondria Cellular respiration √ √
Chloroplasts Photosynthesis √
Vacuoles Storage, secretion √ √
Here's an obvious question: Since cells are capable of all living processes, why are there so many
complex organisms? Why aren’t we just giant cells? The main reason is that as cells grow, the volume
increases faster than the surface membrane, and the membrane is unable to supply food or remove
wastes sufficiently to support the cell; thus cells cooperate in order for larger organisms to develop.
Tissues are groups of cells of any given type (muscle, nerve, etc.) that form the organs of living plants
and animals. Organs have specific functions yet generally work in conjunction with other organs to
comprise body systems such as the cardiovascular system, the nervous system, the digestive system, the
immune system, etc. Very simple organisms may not have as complex a structure or may have more
primitive systems to carry out life processes.
See below for a general review of the body’s structure.