Page 300 - ABCTE Study Guide_Neat
P. 300
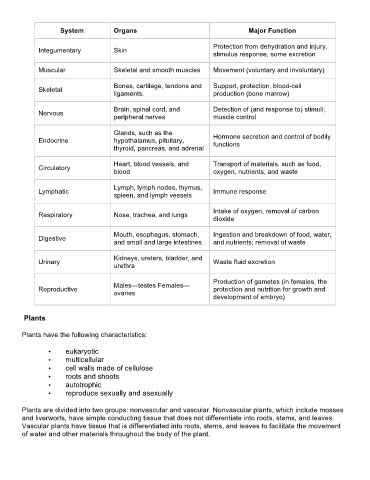
System Organs Major Function
Protection from dehydration and injury,
Integumentary Skin
stimulus response, some excretion
Muscular Skeletal and smooth muscles Movement (voluntary and involuntary)
Bones, cartilage, tendons and Support, protection, blood-cell
Skeletal
ligaments. production (bone marrow)
Brain, spinal cord, and Detection of (and response to) stimuli;
Nervous
peripheral nerves muscle control
Glands, such as the Hormone secretion and control of bodily
Endocrine hypothalamus, pituitary, functions
thyroid, pancreas, and adrenal
Heart, blood vessels, and Transport of materials, such as food,
Circulatory
blood oxygen, nutrients, and waste
Lymph, lymph nodes, thymus,
Lymphatic Immune response
spleen, and lymph vessels
Intake of oxygen, removal of carbon
Respiratory Nose, trachea, and lungs
dioxide
Mouth, esophagus, stomach, Ingestion and breakdown of food, water,
Digestive
and small and large intestines and nutrients; removal of waste
Kidneys, ureters, bladder, and
Urinary Waste fluid excretion
urethra
Production of gametes (in females, the
Males—testes Females—
Reproductive protection and nutrition for growth and
ovaries
development of embryo)
Plants
Plants have the following characteristics:
• eukaryotic
• multicellular
• cell walls made of cellulose
• roots and shoots
• autotrophic
• reproduce sexually and asexually
Plants are divided into two groups: nonvascular and vascular. Nonvascular plants, which include mosses
and liverworts, have simple conducting tissue that does not differentiate into roots, stems, and leaves.
Vascular plants have tissue that is differentiated into roots, stems, and leaves to facilitate the movement
of water and other materials throughout the body of the plant.