Page 126 - Medicinal Chemistry Self Assessment
P. 126
2.5 Drug Binding Interactions 115
Continued from previous page
Phenol Tolterodine Both Serine, threonine, cysteine, tyrosine, glutamic
acid, aspartic acid, lysine, arginine, asparagine,
glutamine, histidine, tryptophan
Tertiary amine Oxybutynin, fesoterodine, tolterodine Acceptor Serine, threonine, cysteine, tyrosine, glutamic
acid, aspartic acid, lysine, arginine, asparagine,
glutamine, histidine, tryptophan
Ester Fesoterodine, oxybutynin Acceptor Serine, threonine, cysteine, tyrosine, glutamic
acid, aspartic acid, lysine, arginine, asparagine,
glutamine, histidine, tryptophan
Note: Please remember that if a functional group is ionized, then it can no longer participate in
hydrogen bonding interactions.
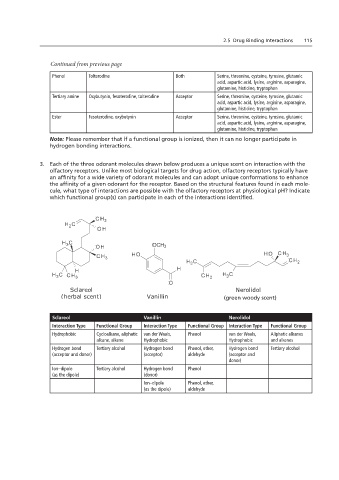
3. Each of the three odorant molecules drawn below produces a unique scent on interaction with the
olfactory receptors. Unlike most biological targets for drug action, olfactory receptors typically have
an affinity for a wide variety of odorant molecules and can adopt unique conformations to enhance
3. Each of the three odorant molecules drawn below produces a unique scent on interaction with the
the affinity of a given odorant for the receptor. Based on the structural features found in each mole-
cule, what type of interactions are possible with the olfactory receptors at physiological pH? Indicate
olfactory receptors. Unlike most biological targets for drug action, olfactory receptors typically have an
which functional group(s) can participate in each of the interactions identified.
Sclareol Nerolidol
(herbal scent) Vanillin (green woody scent)
(green woody scent)
Sclareol Vanillin Nerolidol
Interaction Type Functional Group Interaction Type Functional Group Interaction Type Functional Group
van der Waals,
Phenol
van der Waals,
Aliphatic alkanes
Cycloalkane, aliphatic
Hydrophobic
4. There are five basic flavors that our taste receptors detect: salty, sour, sweet, bitter, and umami
alkane, alkene Hydrophobic Hydrophobic and alkenes
(savory). The taste receptors are located on taste buds that are on our tongue, soft palate, epiglottis, and
Hydrogen bond
Phenol, ether,
Tertiary alcohol
Tertiary alcohol
Hydrogen bond
Hydrogen bond
(acceptor and donor) (acceptor) aldehyde (acceptor and
donor)
Ion–dipole Tertiary alcohol Hydrogen bond Phenol
(as the dipole) CO H (donor)
2
Ion–dipole Phenol, ether,
(as the dipole) aldehyde
H 2 N CO H
2
Glutamic Acid Cucumber flavor Green Pepper Flavor
O
N N H
O
H O P N N
H O O O
OH
H O
Shitaki Mushrooms
Inosinic Acid