Page 53 - Medicinal Chemistry Self Assessment
P. 53
Replacement structure for the answer to question 2 in Chapter 2.9 (Aripiprazole)
42 Medicinal Chemistry Self Assessment
2. The normal pK range for sulfonylureas is 5 to 6. When comparing the pK values of chlorpropamide
Alkyl (aliphatic) chain
a
a
and tolbutamide, it is found that the sulfonylurea of one of these drug molecules has a pK =5.4 and
(Lipid soluble)
a
Ether oxygen
the other has a pK =4.9. Evaluate the structures of these two drug molecules, assign the pK values to
a
a
(Water soluble)
the correct molecules, and provide an explanation for the difference in pK values. Amide
Halogens
a
(Lipid soluble) (Water soluble)
3. Using your answer from question 2, calculate the percent of tolbutamide that will be ionized at an
Hydrocarbon portion
intestinal pH=6.1.
of bicyclic ring
(Lipid soluble)
Aromatic (phenyl) ring
(Lipid soluble)
4. The mechanism of action of this class of drugs involves the ability to interact with the ATP-sensitive
potassium channels in the pancreas. Using the structure of tolbutamide, identify the types of binding
Aripiprazole
interactions that are possible between its functional groups and a protein ion channel. Also identify
amino acids present within this ion channel whose side chains could participate in the interactions
identified. Assume a plasma pH=7.4 for all ionizable functional groups.
Alkyl (aliphatic) chain
(Lipid soluble)
5. Tolbutamide has a half-life of 4.5 to 6.5 hours, whereas chlorpropamide has a half-life of 36 hours.
Propose a chemical/structural reason why chlorpropamide has a significantly longer half-life than
tolbutamide.
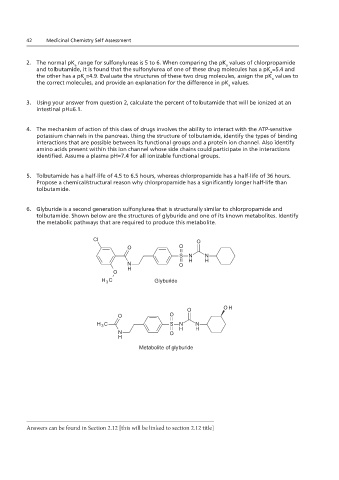
Replacement structure for question 6 in BOTH Chapters 1.12 and 2.12 (Chlorpropamide and Other
Sulfonylureas)
6. Glyburide is a second generation sulfonylurea that is structurally similar to chlorpropamide and
tolbutamide. Shown below are the structures of glyburide and one of its known metabolites. Identify
the metabolic pathways that are required to produce this metabolite.
Cl O
O O
S N N
N O H H
O H
H 3 C Glyburide
O OH
O O
H 3 C S N N
N O H H
H
Metabolite of glyburide
Answers can be found in Section 2.12 [this will be linked to section 2.12 title]