Page 54 - Medicinal Chemistry Self Assessment
P. 54
Section 2 Whole Molecule Drug Evaluation
1.13 Dabigatran Etexilate
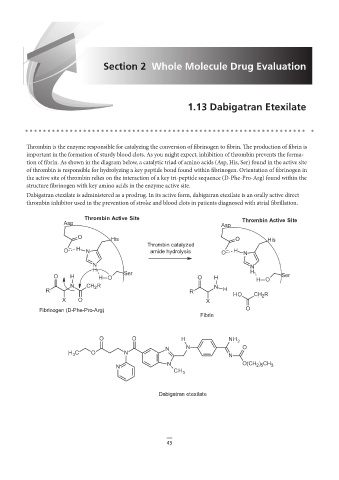
Thrombin is the enzyme responsible for catalyzing the conversion of fibrinogen to fibrin. The production of fibrin is
important in the formation of sturdy blood clots. As you might expect, inhibition of thrombin prevents the forma-
tion of fibrin. As shown in the diagram below, a catalytic triad of amino acids (Asp, His, Ser) found in the active site
of thrombin is responsible for hydrolyzing a key peptide bond found within fibrinogen. Orientation of fibrinogen in
Chapters 1.13/2.13 Concern about His (revised diagram + removed bolded names)
the active site of thrombin relies on the interaction of a key tri-peptide sequence (D-Phe-Pro-Arg) found within the
structure fibrinogen with key amino acids in the enzyme active site.
Chapters 1.13/2.13 Concern about His (revised diagram + removed bolded names)
Dabigatran etexilate is administered as a prodrug. In its active form, dabigatran etexilate is an orally active direct
Thrombin Active Site
thrombin inhibitor used in the prevention of stroke and blood clots in patients diagnosed with atrial fibrillation.
Thrombin Active Site
Thrombin Active Site Thrombin Active Site
Thrombin catalyzed
amide hydrolysis
Thrombin catalyzed
amide hydrolysis
Fibrinogen (D-Phe-Pro-Arg)
Fibrin
Fibrinogen (D-Phe-Pro-Arg)
Chapters 1.13/2.13 (removed bold in drug name) Fibrin
Chapters 1.13/2.13 (removed bold in drug name)
Dabigatran etexilate
Dabigatran etexilate
Chapters 1.13/2.13 (removed bold and centered text)
Chapters 1.13/2.13 (removed bold and centered text)
3 43
3
1 2
1 2
D-Phe-Pro-Arg Tripeptide Sequence
D-Phe-Pro-Arg Tripeptide Sequence