Page 55 - Medicinal Chemistry Self Assessment
P. 55
Chapters 1.13/2.13 Concern about His (revised diagram + removed bolded names)
44 Medicinal Chemistry Self Assessment
Thrombin Active Site
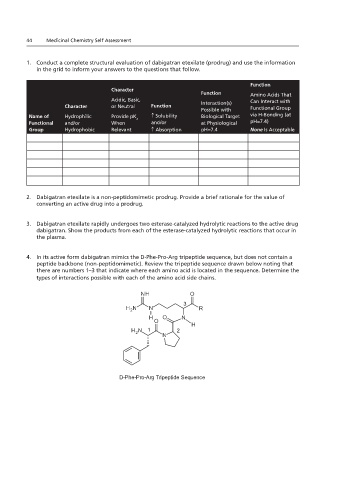
1. Conduct a complete structural evaluation of dabigatran etexilate (prodrug) and use the information Thrombin Active Site
in the grid to inform your answers to the questions that follow.
Function
Thrombin catalyzed
Character
Function amide hydrolysis
Amino Acids That
Acidic, Basic, Interaction(s) Can Interact with
Character or Neutral Function Functional Group
Possible with
Name of Hydrophilic Provide pK ↑ Solubility Biological Target via H-Bonding (at
a
Functional and/or When and/or at Physiological pH=7.4)
Group Hydrophobic Relevant ↑ Absorption pH=7.4 None Is Acceptable
Fibrinogen (D-Phe-Pro-Arg)
Fibrin
Chapters 1.13/2.13 (removed bold in drug name)
2. Dabigatran etexilate is a non-peptidomimetic prodrug. Provide a brief rationale for the value of
converting an active drug into a prodrug.
3. Dabigatran etexilate rapidly undergoes two esterase-catalyzed hydrolytic reactions to the active drug
dabigatran. Show the products from each of the esterase-catalyzed hydrolytic reactions that occur in
the plasma.
Dabigatran etexilate
4. In its active form dabigatran mimics the D-Phe-Pro-Arg tripeptide sequence, but does not contain a
peptide backbone (non-peptidomimetic). Review the tripeptide sequence drawn below noting that
there are numbers 1–3 that indicate where each amino acid is located in the sequence. Determine the
Chapters 1.13/2.13 (removed bold and centered text)
types of interactions possible with each of the amino acid side chains.
3
1 2
D-Phe-Pro-Arg Tripeptide Sequence