Page 44 - GPHS Environmental Public Health Standards (Foundation of Public Health) v1
P. 44
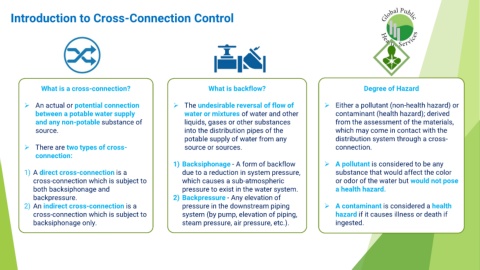
Introduction to Cross-Connection Control
What is a cross-connection? What is backflow? Degree of Hazard
➢ An actual or potential connection ➢ The undesirable reversal of flow of ➢ Either a pollutant (non-health hazard) or
between a potable water supply water or mixtures of water and other contaminant (health hazard); derived
and any non-potable substance of liquids, gases or other substances from the assessment of the materials,
source. into the distribution pipes of the which may come in contact with the
potable supply of water from any distribution system through a cross-
➢ There are two types of cross- source or sources. connection.
connection:
1) Backsiphonage - A form of backflow ➢ A pollutant is considered to be any
1) A direct cross-connection is a due to a reduction in system pressure, substance that would affect the color
cross-connection which is subject to which causes a sub-atmospheric or odor of the water but would not pose
both backsiphonage and pressure to exist in the water system. a health hazard.
backpressure. 2) Backpressure - Any elevation of
2) An indirect cross-connection is a pressure in the downstream piping ➢ A contaminant is considered a health
cross-connection which is subject to system (by pump, elevation of piping, hazard if it causes illness or death if
backsiphonage only. steam pressure, air pressure, etc.). ingested.