Page 41 - Pharmacognosy 2 PG303
P. 41
Pharmacognosy-2 (PG303) Level 2 Clinical Pharmacy-Pharm D
Fruit introduction
Definition:
It is developed ovary or ovaries of a single flower or of a whole inflorescence.
Fruit is a mature fertilized ovary.
function:
protect, nourish and insure the distribution of the seed.
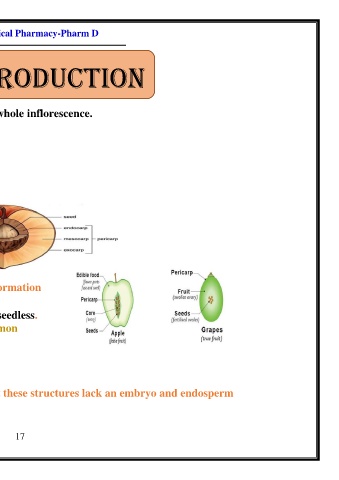
Fruit composed of:
1-pericarp 2-seed
➢ Pericarp composed of three layers:
1-exocarp (epicarp)=outer layer
2-Mesocarp=middle layer
3-endocarp= inner layer
Types of fruit:
1-True fruits: formed from the gynoecium
2-False fruits: other parts of the flower contribute to its formation
➢ Parthenocarpy:
Development of fruit without fertilization, so the fruit is seedless.
Ex: pineapple, banana, cucumber, grape, orange, persimmon
✓ Results from one of three causes:
1-lack of pollination
2-pollination occurs but fertilization does not
3-fertilization is followed by embryo (seed) abortion.
Thus, fruits of cucumber contain seed-like structures, but these structures lack an embryo and endosperm
17