Page 43 - Banking Finance August 2023
P. 43
FEATURES
Hasten deposit insurance
reforms
he recently released Financial Stability Report systems. But the impact could have been contained, if the
T (Issue No 27) of the RBI has accorded enhanced uninsured depositors, who were competent to track their
coverage to ‘deposit insurance’ (DI). For instance,
banks’ affairs, had abstained from digital transfers of their
‘Deposit insurance’ occurs 27 times in the latest
it on social media. This prompted the small depositors to follow
FSR as against zero to 18 times in Issue No 7 (June 2013) to deposits from the weakening banks, and tom-tomming about
Issue No 26 (December 2022). suit, which triggered the runs.
The background to this welcome feature is sourced from the Certainly, the Indian banking system is stronger today than
recent bank failures in the US — Silicon Valley Bank and before. However, from the DI viewpoint, the trend in the
Signature Bank — which were resolved quickly with number and incidence of uninsured depositors and their
interventions from the Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation
deposits, particularly after the DI limit was hiked to Rs. 5 lakh
(FDIC) and the Federal Reserve Board. This could be
in 2020, evokes concern.
accomplished because the US has established systems and
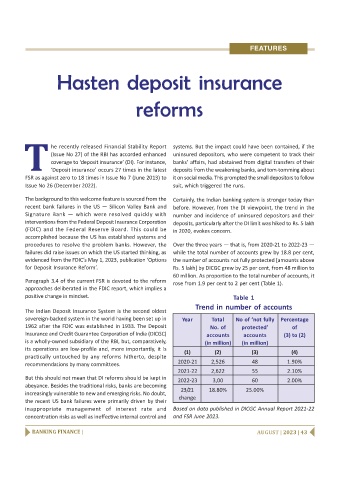
procedures to resolve the problem banks. However, the Over the three years — that is, from 2020-21 to 2022-23 —
failures did raise issues on which the US started thinking, as while the total number of accounts grew by 18.8 per cent,
evidenced from the FDIC’s May 1, 2023, publication ‘Options the number of accounts not fully protected [amounts above
for Deposit Insurance Reform’. Rs. 5 lakh] by DICGC grew by 25 per cent, from 48 million to
60 million. As proportion to the total number of accounts, it
Paragraph 3.4 of the current FSR is devoted to the reform
rose from 1.9 per cent to 2 per cent (Table 1).
approaches deliberated in the FDIC report, which implies a
positive change in mindset.
Table 1
Trend in number of accounts
The Indian Deposit Insurance System is the second oldest
sovereign-backed system in the world having been set up in Year Total No of ‘not fully Percentage
1962 after the FDIC was established in 1933. The Deposit No. of protected’ of
Insurance and Credit Guarantee Corporation of India (DICGC)
accounts accounts (3) to (2)
is a wholly-owned subsidiary of the RBI, but, comparatively, (in million) (in million)
its operations are low-profile and, more importantly, it is
(1) (2) (3) (4)
practically untouched by any reforms hitherto, despite
2020-21 2,526 48 1.90%
recommendations by many committees.
2021-22 2,622 55 2.10%
But this should not mean that DI reforms should be kept in
2022-23 3,00 60 2.00%
abeyance. Besides the traditional risks, banks are becoming
23/21 18.80% 25.00%
increasingly vulnerable to new and emerging risks. No doubt,
change
the recent US bank failures were primarily driven by their
inappropriate management of interest rate and Based on data published in DICGC Annual Report 2021-22
concentration risks as well as ineffective internal control and and FSR June 2023.
BANKING FINANCE | AUGUST | 2023 | 43