Page 44 - Banking Finance August 2023
P. 44
FEATURES
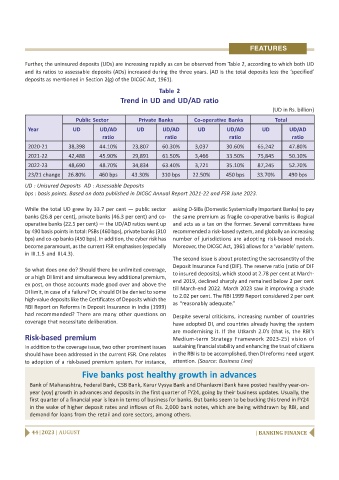
Further, the uninsured deposits (UDs) are increasing rapidly as can be observed from Table 2, according to which both UD
and its ratios to assessable deposits (ADs) increased during the three years. (AD is the total deposits less the ‘specified’
deposits as mentioned in Section 2(g) of the DICGC Act, 1961).
Table 2
Trend in UD and UD/AD ratio
(UD in Rs. billion)
Public Sector Private Banks Co-operative Banks Total
Year UD UD/AD UD UD/AD UD UD/AD UD UD/AD
ratio ratio ratio ratio
2020-21 38,398 44.10% 23,807 60.30% 3,037 30.60% 65,242 47.80%
2021-22 42,488 45.90% 29,891 61.50% 3,466 33.50% 75,845 50.10%
2022-23 48,690 48.70% 34,834 63.40% 3,721 35.10% 87,245 52.70%
23/21 change 26.80% 460 bps 43.30% 310 bps 22.50% 450 bps 33.70% 490 bps
UD : Unisured Deposits AD : Assessable Deposits
bps : basis points. Based on data published in DICGC Annual Report 2021-22 and FSR June 2023.
While the total UD grew by 33.7 per cent — public sector asking D-SIBs (Domestic Systemically Important Banks) to pay
banks (26.8 per cent), private banks (46.3 per cent) and co- the same premium as fragile co-operative banks is illogical
operative banks (22.5 per cent) — the UD/AD ratios went up and acts as a tax on the former. Several committees have
by 490 basis points in total: PSBs (460 bps), private banks (310 recommended a risk-based system, and globally an increasing
bps) and co-op banks (450 bps). In addition, the cyber risk has number of jurisdictions are adopting risk-based models.
become paramount, as the current FSR emphasises (especially Moreover, the DICGC Act, 1961 allows for a ‘variable’ system.
in III.1.5 and III.4.3).
The second issue is about protecting the sacrosanctity of the
Deposit Insurance Fund (DIF). The reserve ratio (ratio of DIF
So what does one do? Should there be unlimited coverage,
to insured deposits), which stood at 2.78 per cent at March-
or a high DI limit and simultaneous levy additional premium,
end 2019, declined sharply and remained below 2 per cent
ex post, on those accounts made good over and above the
till March-end 2022. March 2023 saw it improving a shade
DI limit, in case of a failure? Or, should DI be denied to some
to 2.02 per cent. The RBI 1999 Report considered 2 per cent
high-value deposits like the Certificates of Deposits which the
as “reasonably adequate.”
RBI Report on Reforms in Deposit Insurance in India (1999)
had recommended? There are many other questions on
Despite several criticisms, increasing number of countries
coverage that necessitate deliberation.
have adopted DI, and countries already having the system
are modernising it. If the Utkarsh 2.0’s (that is, the RBI’s
Risk-based premium Medium-term Strategy Framework 2023-25) vision of
In addition to the coverage issue, two other prominent issues sustaining financial stability and enhancing the trust of citizens
should have been addressed in the current FSR. One relates in the RBI is to be accomplished, then DI reforms need urgent
to adoption of a risk-based premium system. For instance, attention. (Source: Business Line)
Five banks post healthy growth in advances
Bank of Maharashtra, Federal Bank, CSB Bank, Karur Vysya Bank and Dhanlaxmi Bank have posted healthy year-on-
year (yoy) growth in advances and deposits in the first quarter of FY24, going by their business updates. Usually, the
first quarter of a financial year is lean in terms of business for banks. But banks seem to be bucking this trend in FY24
in the wake of higher deposit rates and inflows of Rs. 2,000 bank notes, which are being withdrawn by RBI, and
demand for loans from the retail and core sectors, among others.
44 | 2023 | AUGUST | BANKING FINANCE