Page 65 - Operations Strategy
P. 65
40 CHAPTER 1 • OPERATiOns sTRATEgy
an operations strategy, but applied across all functions and domains of the organisa-
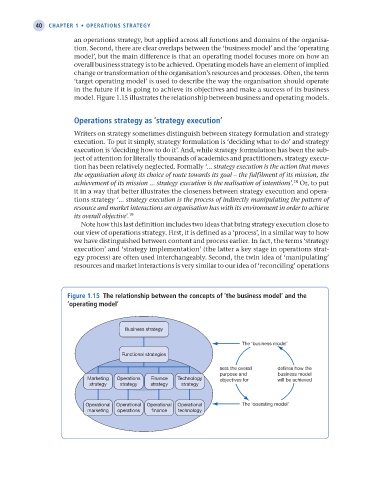
tion. Second, there are clear overlaps between the ‘business model’ and the ‘operating
model’, but the main difference is that an operating model focuses more on how an
overall business strategy is to be achieved. Operating models have an element of implied
change or transformation of the organisation’s resources and processes. Often, the term
‘target operating model’ is used to describe the way the organisation should operate
in the future if it is going to achieve its objectives and make a success of its business
model. Figure 1.15 illustrates the relationship between business and operating models.
Operations strategy as ‘strategy execution’
Writers on strategy sometimes distinguish between strategy formulation and strategy
execution. To put it simply, strategy formulation is ‘deciding what to do’ and strategy
execution is ‘deciding how to do it’. And, while strategy formulation has been the sub-
ject of attention for literally thousands of academics and practitioners, strategy execu-
tion has been relatively neglected. Formally ‘… strategy execution is the action that moves
the organisation along its choice of route towards its goal – the fulfilment of its mission, the
18
achievement of its mission … strategy execution is the realisation of intentions ’. Or, to put
it in a way that better illustrates the closeness between strategy execution and opera-
tions strategy ‘… strategy execution is the process of indirectly manipulating the pattern of
resource and market interactions an organisation has with its environment in order to achieve
19
its overall objective ’.
Note how this last definition includes two ideas that bring strategy execution close to
our view of operations strategy. First, it is defined as a ‘process’, in a similar way to how
we have distinguished between content and process earlier. In fact, the terms ‘strategy
execution’ and ‘strategy implementation’ (the latter a key stage in operations strat-
egy process) are often used interchangeably. Second, the twin idea of ‘manipulating’
resources and market interactions is very similar to our idea of ‘reconciling’ operations
Figure 1.15 the relationship between the concepts of ‘the business model’ and the
‘operating model’
Business strategy
The ‘business model’
Functional strategies
sets the overall defines how the
purpose and business model
Marketing Operations Finance Technology objectives for will be achieved
strategy strategy strategy strategy
Operational Operational Operational Operational The ‘operating model’
marketing operations finance technology
M01 Operations Strategy 62492.indd 40 02/03/2017 13:00