Page 165 - Libro 2
P. 165
9 — Duplex Ultrasound of Lower Extremity Arteries
145
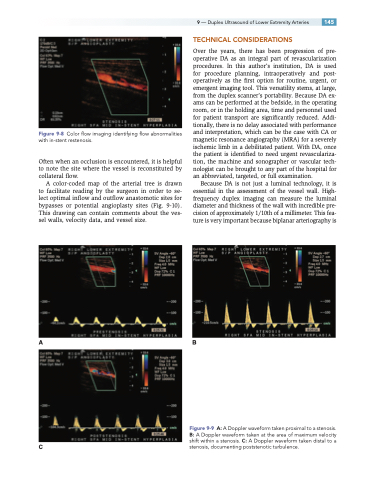
Figure 9-8 Color flow imaging identifying flow abnormalities with in-stent restenosis.
Often when an occlusion is encountered, it is helpful to note the site where the vessel is reconstituted by collateral flow.
A color-coded map of the arterial tree is drawn to facilitate reading by the surgeon in order to se- lect optimal inflow and outflow anastomotic sites for bypasses or potential angioplasty sites (Fig. 9-10). This drawing can contain comments about the ves- sel walls, velocity data, and vessel size.
TECHNICAL CONSIDERATIONS
Over the years, there has been progression of pre- operative DA as an integral part of revascularization procedures. In this author’s institution, DA is used for procedure planning, intraoperatively and post- operatively as the first option for routine, urgent, or emergent imaging tool. This versatility stems, at large, from the duplex scanner’s portability. Because DA ex- ams can be performed at the bedside, in the operating room, or in the holding area, time and personnel used for patient transport are significantly reduced. Addi- tionally, there is no delay associated with performance and interpretation, which can be the case with CA or magnetic resonance angiography (MRA) for a severely ischemic limb in a debilitated patient. With DA, once the patient is identified to need urgent revasculariza- tion, the machine and sonographer or vascular tech- nologist can be brought to any part of the hospital for an abbreviated, targeted, or full examination.
Because DA is not just a luminal technology, it is essential in the assessment of the vessel wall. High- frequency duplex imaging can measure the luminal diameter and thickness of the wall with incredible pre- cision of approximately 1/10th of a millimeter. This fea- ture is very important because biplanar arteriography is
AB
Figure 9-9 A: A Doppler waveform taken proximal to a stenosis. B: A Doppler waveform taken at the area of maximum velocity shift within a stenosis. C: A Doppler waveform taken distal to a
C stenosis, documenting poststenotic turbulence.