Page 235 - Libro 2
P. 235
14 — Duplex Imaging of the Lower Extremity Venous System
215
Figure 14-7 A transverse view of the superficial femoral artery (SFA) and femoral vein (FV ) with the medial aspect of the thigh.
At the adductor canal, the FV travels deep to the muscles of the thigh. Distal to the adductor canal, the vein is called the popliteal vein.
Popliteal Vein
The popliteal vein is the main drainage for blood leav- ing the calf (Figs. 14-10 and 14-11). In the upper por- tion of the popliteal fossa, the popliteal vein and artery are the only vessels visualized. As was the case with the FV, the popliteal vein can occasionally be bifid.
Anterior Tibial Vein
The anterior tibial vein (ATV) terminates into the popliteal vein in the mid to upper regions of the pop- liteal fossa. However, this is not commonly seen on
Figure 14-8 A longitudinal view in color of the superficial femoral artery (SFA) and femoral vein (FV ) within the mid-thigh.
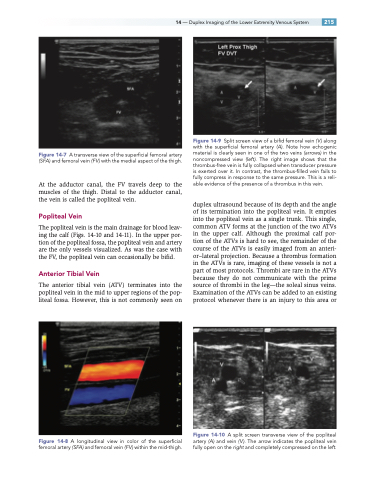
Figure 14-9 Split screen view of a bifid femoral vein ( V ) along with the superficial femoral artery (A). Note how echogenic material is clearly seen in one of the two veins (arrows) in the noncompressed view (left). The right image shows that the thrombus-free vein is fully collapsed when transducer pressure is exerted over it. In contrast, the thrombus-filled vein fails to fully compress in response to the same pressure. This is a reli- able evidence of the presence of a thrombus in this vein.
duplex ultrasound because of its depth and the angle of its termination into the popliteal vein. It empties into the popliteal vein as a single trunk. This single, common ATV forms at the junction of the two ATVs in the upper calf. Although the proximal calf por- tion of the ATVs is hard to see, the remainder of the course of the ATVs is easily imaged from an anteri- or–lateral projection. Because a thrombus formation in the ATVs is rare, imaging of these vessels is not a part of most protocols. Thrombi are rare in the ATVs because they do not communicate with the prime source of thrombi in the leg—the soleal sinus veins. Examination of the ATVs can be added to an existing protocol whenever there is an injury to this area or
Figure 14-10 A split screen transverse view of the popliteal artery (A) and vein ( V ). The arrow indicates the popliteal vein fully open on the right and completely compressed on the left.