Page 237 - Libro 2
P. 237
14 — Duplex Imaging of the Lower Extremity Venous System
217
Figure 14-14 A transverse view of the common posterior tibial and common peroneal trunks.
paired posterior tibial veins unite to form the com- mon tibial trunk, and the paired peroneal veins unite to form the common peroneal trunk. The specific length of these two common trunks is variable.
Posterior Tibial Veins
The posterior tibial veins (PTVs) will course medially in the calf near the tibia. The veins are paired follow- ing the posterior tibial artery (Fig. 14-16). They arise via tributaries between the medial malleolus and the Achilles tendon at the ankle.
Peroneal Veins
The peroneal veins are followed deeper in the calf (Fig. 14-17) as they parallel the PTVs through most
Figure 14-15 A transverse view of the common posterior tibial and common peroneal trunks with color added.
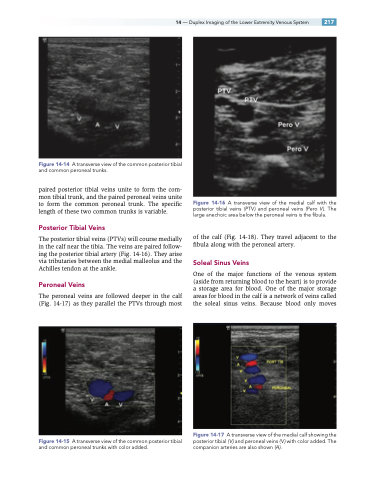
Figure 14-16 A transverse view of the medial calf with the posterior tibial veins (PTV ) and peroneal veins (Pero V ). The large anechoic area below the peroneal veins is the fibula.
of the calf (Fig. 14-18). They travel adjacent to the fibula along with the peroneal artery.
Soleal Sinus Veins
One of the major functions of the venous system (aside from returning blood to the heart) is to provide a storage area for blood. One of the major storage areas for blood in the calf is a network of veins called the soleal sinus veins. Because blood only moves
Figure 14-17 A transverse view of the medial calf showing the posterior tibial ( V ) and peroneal veins ( V ) with color added. The companion arteries are also shown (A).