Page 433 - Libro 2
P. 433
27 — Vascular Applications of Ultrasound Contrast Agents
413
AB
C
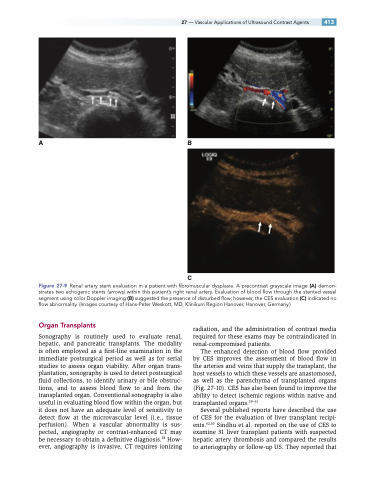
Figure 27-9 Renal artery stent evaluation in a patient with fibromuscular dysplasia. A precontrast grayscale image (A) demon- strates two echogenic stents (arrows) within this patient’s right renal artery. Evaluation of blood flow through the stented vessel segment using color Doppler imaging (B) suggested the presence of disturbed flow; however, the CES evaluation (C) indicated no flow abnormality. (Images courtesy of Hans-Peter Weskott, MD, Klinikum Region Hanover, Hanover, Germany.)
Organ Transplants
Sonography is routinely used to evaluate renal, hepatic, and pancreatic transplants. The modality is often employed as a first-line examination in the immediate postsurgical period as well as for serial studies to assess organ viability. After organ trans- plantation, sonography is used to detect postsurgical fluid collections, to identify urinary or bile obstruc- tions, and to assess blood flow to and from the transplanted organ. Conventional sonography is also useful in evaluating blood flow within the organ, but it does not have an adequate level of sensitivity to detect flow at the microvascular level (i.e., tissue perfusion). When a vascular abnormality is sus- pected, angiography or contrast-enhanced CT may be necessary to obtain a definitive diagnosis.58 How- ever, angiography is invasive, CT requires ionizing
radiation, and the administration of contrast media required for these exams may be contraindicated in renal-compromised patients.
The enhanced detection of blood flow provided by CES improves the assessment of blood flow in the arteries and veins that supply the transplant, the host vessels to which these vessels are anastomosed, as well as the parenchyma of transplanted organs (Fig. 27-10). CES has also been found to improve the ability to detect ischemic regions within native and transplanted organs.59–61
Several published reports have described the use of CES for the evaluation of liver transplant recipi- ents.62,63 Sindhu et al. reported on the use of CES to examine 31 liver transplant patients with suspected hepatic artery thrombosis and compared the results to arteriography or follow-up US. They reported that